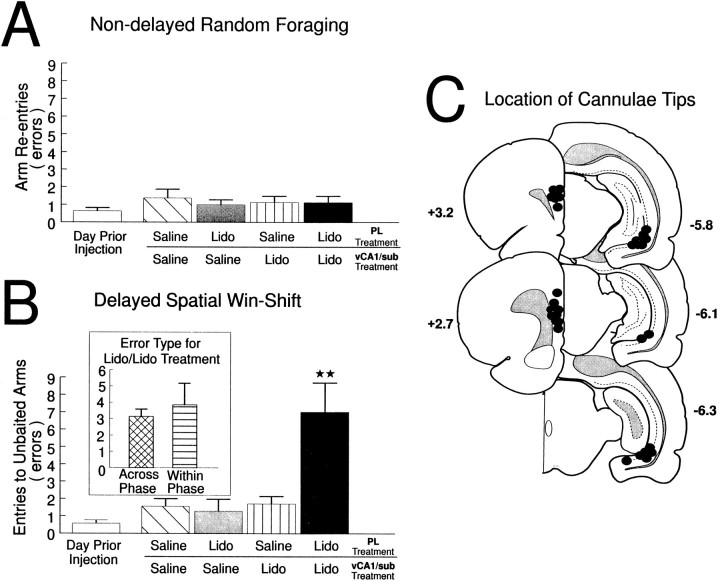
Fig. 4.
The effects of PL–vSub disconnections on performance of a radial-arm maze test battery. A, Nondelayed random foraging. Number of errors (mean ± SEM) made by rats on the day before the first injection (open bar), after unilateral infusions of saline into both the PL and the vSub (hatched bar), unilateral infusions of lidocaine (Lido) into the PL and contralateral saline in the vSub (gray bar), unilateral infusions of Lido into the vSub and contralateral saline into the PL (stripped bar), and unilateral Lido into the vSub and contralateral Lido into the PL (disconnection; black bar) before the nondelayed RF task. B, Delayed spatial win-shift. Number of errors (mean ± SEM) made by rats on the day before the first injection (open bar), after unilateral infusions of saline into both the PL and the vSub (hatched bar), unilateral infusions of lidocaine (Lido) into the PL and contralateral saline in the vSub (gray bar), unilateral infusions of Lido into the vSub and contralateral saline into the PL (stripped bar), and unilateral Lido into the vSub and contralateral Lido into the PL (disconnection; black bar) before the test phase of the delayed SWSh task. **p < 0.001 versus all other treatment conditions.Inset shows number of across-phase (cross-hatched bar) versus within-phase (horizontal-stripped bar) errors made by rats during Lido/Lido (disconnection) injection days. C, Location of cannulae tips (black circles) for all rats used for data analysis receiving PL–vSub disconnections before either the nondelayed RF task or the delayed SWSh task. Plates are computer-generated adaptations from Swanson (1992) that were modified to resemble those from Paxinos and Watson (1986).Numbers beside each plate correspond to millimeters from bregma. For clarity, C represents the location of cannulae tips on sides that received infusions on disconnection injection days. All animals received infusions of either lidocaine or saline in each hemisphere.