Fig. 4.
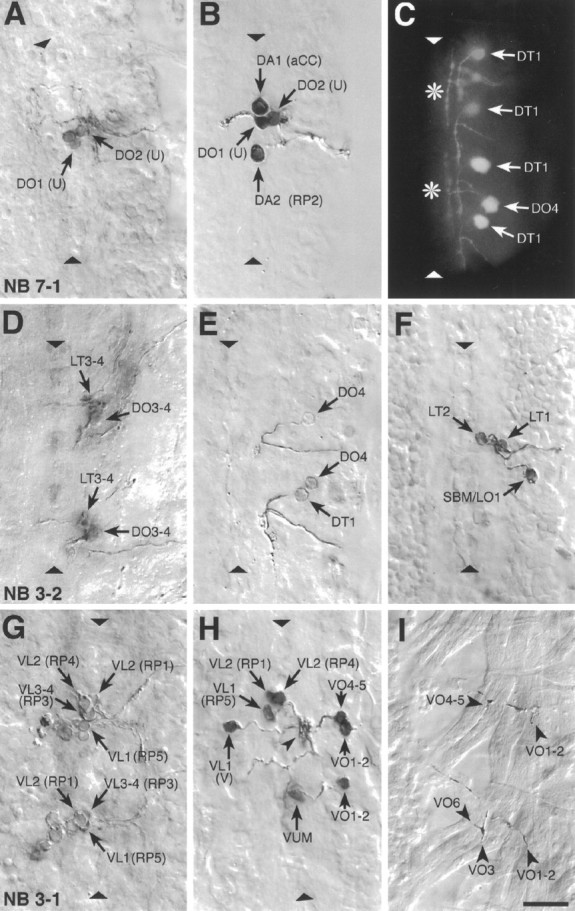
Examples of photoconverted preparations of clones from individually labeled NBs and of retrogradely labeled motorneurons. Photoconverted DiI preparations of clones from individual, identified, labeled NBs (A, D, G), of motorneurons (B, E, F, H), and of NMJs (I), and a fluorescent image of DiI-labeled motorneurons (C) are shown. The images are collages of several focal planes, which were assembled with Photoshop; the dorsal focal plane is uppermost.A, The two medial U motorneurons and the fpCC interneuron derived from NB 7-1. The other motorneurons derived from NB 7-1 (the two mediolateral U neurons and the motorneurons that most likely innervate muscles VO4-6) are not visible in this focal plane.B, The motorneurons that innervate the four dorsal muscles DA1-2 (aCC and RP2) and DO1-2 (the two medial U neurons) were retrogradely labeled in one abdominal segment. C, A fluorescent image of the motorneuron innervating muscle DT1, which was labeled in four adjacent abdominal segments. Note the characteristic cell body position and dendritic projection. Theasterisks indicate T-shaped sensory axons that were labeled by chance in two of the segments. The motorneuron that innervates muscle DO4 was labeled in one segment. D, Motorneurons derived from two NB 3-2 clones. The anterior clone is thoracic (T3); the posterior clone is abdominal (A2). NB 3-2 gives rise to two morphological types of motorneurons: first, motorneurons that project through the ISN and innervate muscles DT1 (not visible in this focal plane), DO3-4, and probably also DO5 (not visible in this focal plane); second, motorneurons that project through SNa and innervate muscle LT3 and probably also LT4. E, A photoconverted preparation similar to the one shown in C. F, Three motorneurons that project through SNa are shown. The motorneurons that innervate muscles LT1-2 are morphologically and clonally distinct from the ones innervating muscles LO1 and SBM. G, Two NB 3-1 clones, of which the anterior clone is thoracic (T3) and the posterior clone is abdominal (A1). NB 3-1 gives rise to the four morphologically similar RP1, -3, -4, and -5 motorneurons that innervate the ventral longitudinal muscles VL1-4.H, Most of the motorneurons that project through SNb and SNd were retrogradely labeled in a single abdominal segment to illustrate their relative cell body positions. In addition, the motorneuron that innervates muscles VO1-2 was labeled in the next posterior segment. Note that the V-neuron is morphologically distinct from the RP neurons but that their dendritic arbors are overlapping (arrowhead) (see text). The VUM neuron lies in the same segment as the muscles that it innervates, whereas the RP and V-neurons as well as the motorneurons that innervate muscles VO1-2 and VO4-5 lie in the next anterior segment. I, The endplates of two VUM neurons on the ventral oblique muscles VO1-6 in two adjacent abdominal segments (the VUMs were retrogradely labeled on the contralateral side). Anterior is up. The ventral midline is indicated by triangles and is on theleft in I. Scale bar, 10 μm.
