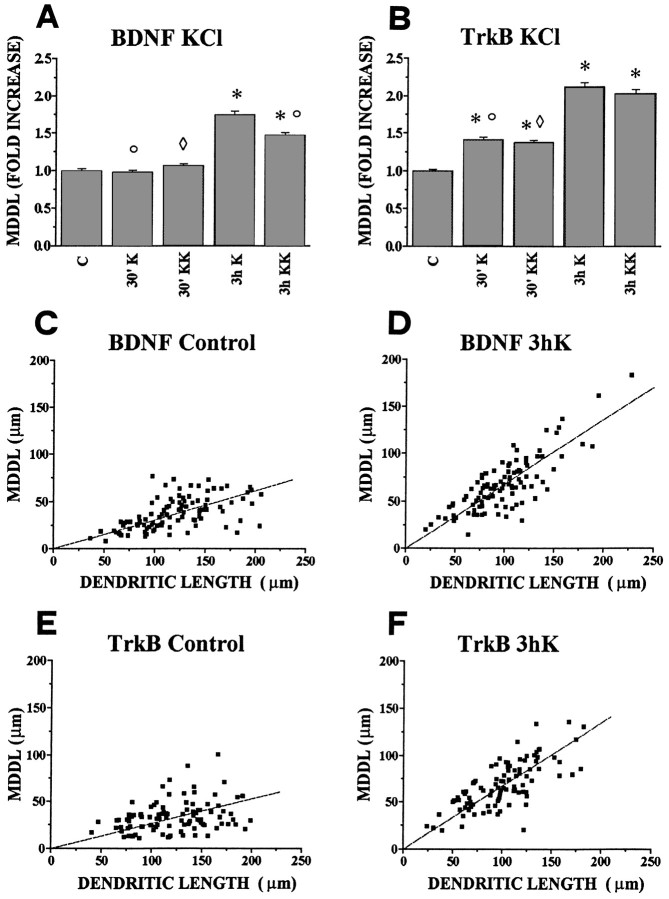
Fig. 4.
Quantitative analysis of dendritic localization of BDNF and TrkB mRNAs after depolarization of hippocampal neurons in culture. Bars in A and Bindicate the fold increase, with respect to controls, of the mean maximal distance at which the in situ labeling in dendrites was detectable (MDDL). A, BDNF mRNA. Depolarization with either 10 (K) or 20 mm KCl (KK) increases the mean maximal distance of dendritic labeling (MDDL) at 3 hr (3 h K and 3 h KK) but not at 30 min (30′ K and 30′ KK). The average MDDL measured with 10 mm KCl (3 h K) is larger than with 20 mm KCl (3 h KK). B, TrkB mRNA. Both KCl concentrations induce a significant increase in MDDL of TrkB mRNA after 30 min (30′ K, 30′ KK) and a stronger increase at 3 hr (3 h K, 3 h KK). ○, Significantly different with respect to the 3 h K-stimulated; ⋄, significantly different with respect to the 3 h KK stimulated; and *, significantly different with respect to the control (no stimulation). Error bars represent SE. The corresponding numerical values, number of dendrites measured, and significance values are shown in Table 1.C, D, E, F, Correlation plots of the MDDL versus dendritic length. Each point refers to one MDDL determination, together with the length of the corresponding dendrite, under the experimental conditions indicated. The scatter plots were fitted by linear regression lines through the origin. C, Slope = 0.30, correlation coefficient r = 0.57; D, slope = 0.68; r = 0.80; E, slope = 0.26; r = 0.31; F, slope = 0.67; r = 0.72.