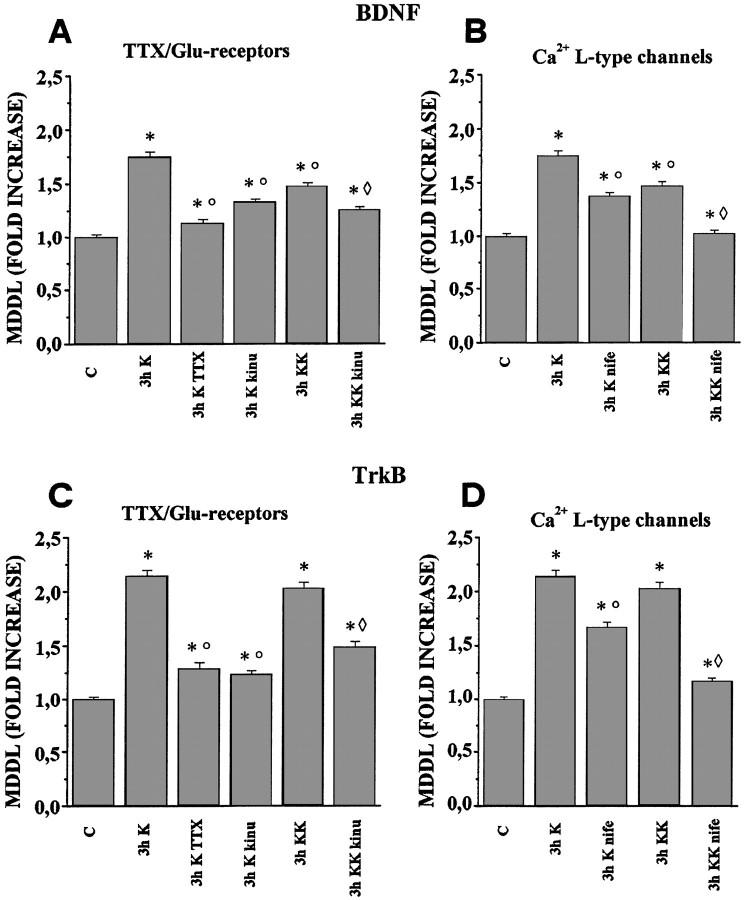
Fig. 7.
Effects of TTX, kinurenic acid, and nifedipine on the KCl-induced increase in dendritic localization of BDNF and TrkB mRNAs. Quantitative analysis of the MDDL for BDNF and TrkB mRNAs in the presence of TTX, kinurenic acid, and nifedipine. Barsindicate the fold increase, with respect to controls, of the mean maximal distance at which the in situ labeling was detectable (MDDL). A, Continuous presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) inhibits the increase in MDDL for BDNF mRNA, induced by depolarization with 10 mmKCl for 3 hr (3h K TTX). The glutamate receptor antagonist kinurenic acid partially counteracts the KCl-induced increase by either 10 (3h K kinu) or 20 mmKCl (3h KK kinu). B, The L-type Ca2+ channel blocker nifedipine has distinct effects at different KCl concentrations, with a partial inhibition at 10 mm KCl (3h K nife) and an almost complete inhibition at 20 mm KCl (3h KK nife).C, TTX strongly inhibits the MDDL increase for TrkB mRNA in 10 mm KCl (3h K TTX). The glutamate receptor antagonist kinurenic acid reduced the 10 mm KCl depolarization effects (3h K kinu) more effectively than at 20 mm KCl (3h KK kinu). D, In contrast, nifedipine almost completely abolishes the effects induced by 20 mm KCl (3h KK nife) and only partially inhibits those induced by 10 mm KCl depolarization (3h K nife). Error bars represent SE. ○, Significantly different with respect to the 3 h K-stimulated; ⋄, significantly different with respect to the 3 h KK stimulated; *, significantly different with respect to the control (no stimulation). Also see Table 1.