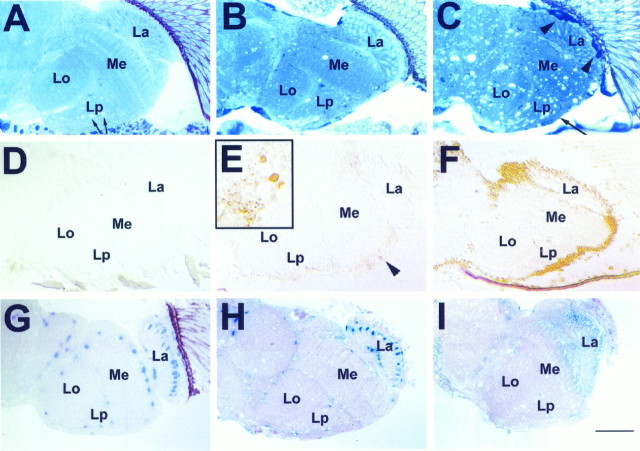
Fig. 1.
Progression of brain degeneration insws flies. A–C, One micrometer horizontal plastic head sections stained with toluidine blue. Vacuolization and darkly stained structures (arrowheadsin C) increase with advancing age. These are accompanied by a thinning of the cortex (long arrow inC). A, Wild type, age 20 d (arrows indicate white areas in the lobula plate that are not vacuoles but cross-sections of giant fibers). B, sws1 5 d old. C, sws1 20 d old. D–F,Apoptosis staining on 8 μm horizontal cryosections. D,Wild type 20 d old. E, In a 5-d-oldsws1 fly, single cells are intensely stained (arrowhead and inset). Single dying cells are already indicated by the dark toluidine blue staining in B (arrows). F, In a 20-d-old sws1 fly, there is widespread staining, suggesting apoptosis in most cortical cell bodies.G–I, Effect of degeneration on LacZ-expressing cells of the glial-specific enhancer–trap line rC56: 1 μm horizontal plastic brain sections stained with X-galactosidase (X-Gal).G, Heterozygous rC56/wild-type fly 10 d old. H, 8-d-oldsws4/y;rC56/wild-type fly. The number of cells showing LacZ staining is decreased. I, Fourteen-day-oldsws4/y;rC56/wild-type brain. The LacZ staining is almost completely absent, indicating loss of expression or degeneration of many glial cells. Brains were dissected and stained with X-Gal and then embedded in plastic, sectioned, and counterstained with pyronin Y. All flies were raised at 25°C. La, Lamina; Me, medulla;Lo, lobula; Lp, lobula plate. Anterior is at the top. Scale bar: A–I, 50 μm;inset in E, 15 μm.