Fig. 3.
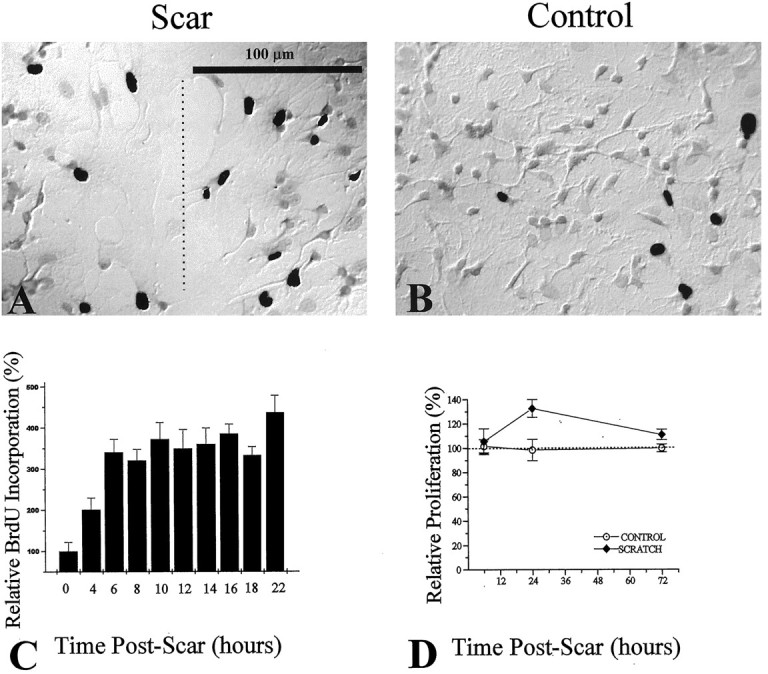
Assessment of scar-associated proliferation, using BrdU and [3H]-thymidine incorporation. BrdU incorporation was visualized by using a biotinylated monoclonal antibody against BrdU and a streptavidin-peroxidase/DAB enzyme reaction. BrdU+ cells are indicated by DAB-reacted cells, which appear as black nuclei in the grayscale photograph. A, After a 2 hr pulse with BrdU labeling reagent, an injury-induced increase in the number of BrdU-positive cells at the region of the scar (dashed line) was observed, as compared with noninjured control cultures (B). C, Ratios of BrdU-positive/total cell number were assessed as a function of time postinjury. Ratios for each time point were normalized to control ratios (control = 0 hr postscar). D, Changes in proliferation were assessed by [3H]-thymidine incorporation relative to control. An increase in proliferation was seen at 24 hr postinjury and peaked at 35% above control proliferation.
