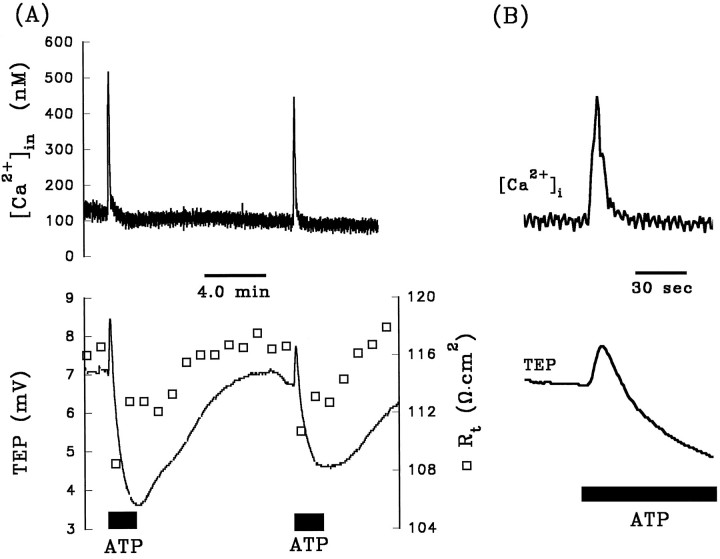
Fig. 4.
A, Effects of two consecutive pulses of 100 μm ATP added to Ringer’s solution perfusing the apical membrane on [Ca2+]in, TEP, and Rt. [Ca2+]in measurements were made with the ratioing dye, fura-2 AM. ATP elicited a large transient increase in [Ca2+]in from ∼120 to 500 nmthat follows a time course similar to the first two phases of the electrical effects of ATP (see text). In addition, [Ca2+]in immediately returned to its initial, resting value, whereas ATP remains in the apical Ringer’s solution (the ATP pulse lasted for 2 min, but the transient increase in [Ca2+]in lasted for only 30–40 sec). The first and second ATP responses were comparable in magnitude and time course, indicating repeatability in the calcium and electrical responses. B, The effects of the second ATP response are replotted at higher gain for purposes of clarity. The same vertical axes are used for [Ca2+]in and TEP in bothA and B.