Fig. 7.
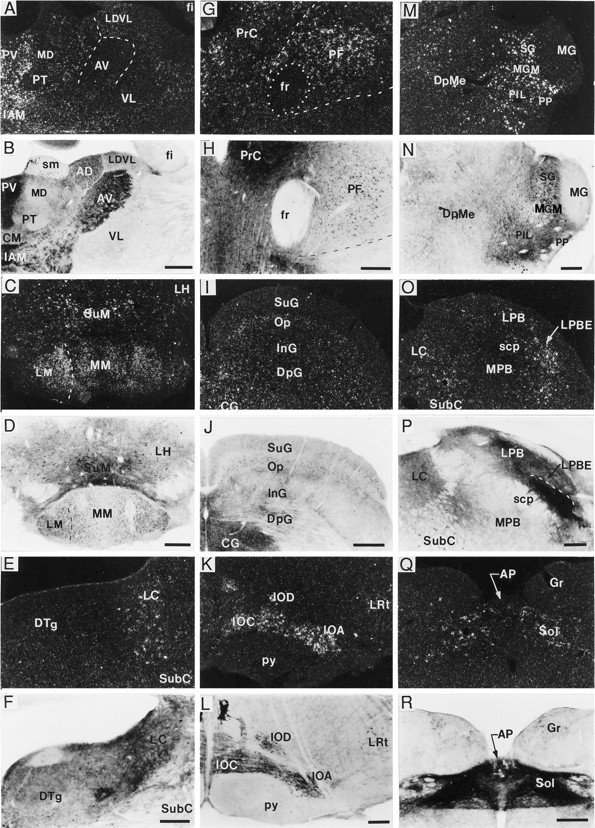
Localization of BDNF-ir and mRNA in thalamic and brainstem regions. Dark-field and bright-field photomicrographs showing BDNF cRNA hybridization (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, O, Q) and BDNF immunolabeling (B, D, F, H, J, L, N, P, R), respectively, in thalamus (A, B), mammillary region (C, D), locus coeruleus (E, F), parafascicular nucleus (PF) (G, H), superior colliculus (I, J), inferior olivary complex (K, L), medial geniculate nucleus (M, N), parabrachial region (O, P), and the nucleus of the solitary tract (Q, R). In many thalamic (A, B, G, H, M, N) and hypothalamic (C, D) areas, the distributions of BDNF mRNA and perikaryal BDNF-ir overlapped; although in some regions [e.g., anteroventral thalamic nucleus (AV)] there was heavy fiber/terminal BDNF-ir in the absence of hybridization (A, B). In other regions, such as the locus coeruleus (LC) (E, F) and nucleus of the solitary tract (Sol) (Q, R), cRNA-labeled cells could be detected, but it was difficult to identify immunostained cells because of the fiber/terminal immunolabeling. Weak labeling with both the cRNA and antibody also overlapped in most layers of superior colliculus, excluding the superficial gray layer, which did not contain cRNA labeling (I, J). In contrast, heavy hybridization and BDNF-ir were detected throughout the inferior olivary complex (K, L). Moderate to heavy BDNF cRNA labeling was found in the external portion of the lateral parabrachial nucleus (LPBE), whereas heavy fiber/terminal BDNF-ir was present in most subregions of the lateral parabrachial subfield (LPB) (O, P); neither cRNA nor antibody labeled the medial portion of the parabrachial nucleus (MPB) (O, P). Scale bars (shown inB, D, J, N): A–D, I, J, M, N, 500 μm, respectively; (shown in F): E, F, 200 μm; (shown in H, P, R): G, H, O, P–R, 250 μm, respectively. AP, Area postrema;CG, central (periaqueductal) gray; DpG, superior colliculus, deep gray layer; DpMe, deep mesencephalic nucleus; DTg, dorsal tegmental nucleus;fr, fasciculus retroflexus; Gr, gracile nucleus; IAM, interanteromedial thalamic nucleus;InG, superior colliculus, intermediate gray layer;IOA, inferior olive, subnucleus A; IOC, inferior olive, subnucleus C; IOD, inferior olive, dorsal nucleus; LDVL, laterodorsal thalamic nucleus, ventrolateral; LH, lateral hypothalamic area;LM, lateral mammillary nucleus; LRt, lateral reticular nucleus; MG, medial geniculate nucleus; MGM, medial geniculate nucleus, medial portion;MM, medial mammillary nucleus; Op, superior colliculus, optic nerve layer; PIL, posterior intralaminar nucleus; PrC, precommissural nucleus; PP, peripeduncular thalamic nucleus;PT, paratenial thalamic nucleus; PV, paraventricular thalamic nucleus; py, pyramidal tract;scp, superior cerebellar peduncle; SG, suprageniculate nucleus; SubC, subcoeruleus nucleus;SuG, superior colliculus, superficial gray layer;SuM, supramammillary nucleus; VL, ventrolateral thalamic nucleus.
