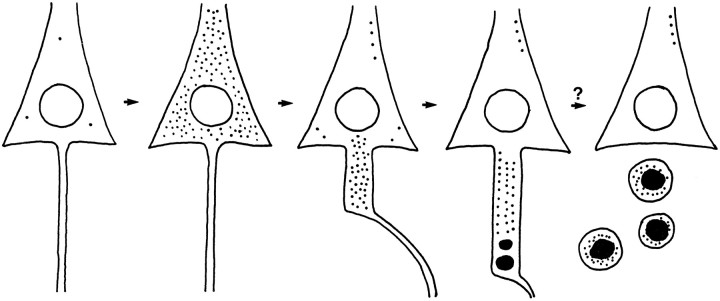
Fig. 11.
Schematic diagram showing a hypothetical sequence of ZPAD-induced alterations on the fine morphology of CA1 neurons. The perikaryal cytosol of a control CA1 pyramidal cell contains only three lysosomes (cell on far left). Six days of exposure to ZPAD, an inhibitor of cathepsins B and L, result in a dramatic expansion of the lysosomal population (second cell in diagram). CA1 neurons allowed to recover for 7 d after ZPAD treatment restore the normal ultrastructure of the soma by sweeping the excess lysosomes and residual bodies into the axon hillock and initial segment (middle neuron). In distal portions of long “meganeurites,” lysosomal bodies are fused into circular aggregates (fourth cell). The last neuron (on thefar right) depicts a hypothesized outcome of this sequence in which subsequent exocytosis of the lysosomal compactions results in pyramidal cell axotomy.