Fig. 2.
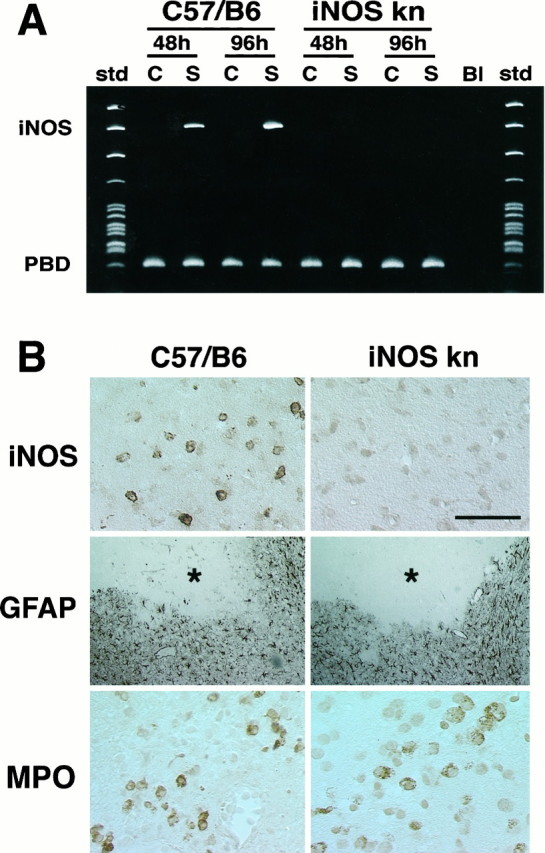
A, iNOS message detected by RT-PCR in wild-type mice (C57/B6) and iNOS knockouts at 48 and 96 hr after ischemia. No iNOS signal is detected in the ischemic brain at either time points. B, Immunoreactivity foriNOS, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), or myeloperoxidase (MPO) in iNOS null mice and controls (C57/B6) 96 hr after MCA occlusion. Cerebral ischemia is followed by expression of iNOS immunoreactivity in C57/B6 mice but not in iNOS knockouts (top panels). Immunoreactivity for the astrocytic marker GFAP (middle panels) is comparable between iNOS null mice and wild-type controls. The asterisk indicates the infarcted area. GFAP expression occurs at the border of the lesion. To detect infiltrating inflammatory cells in the post-ischemic brain, immunocytochemistry for MPO, an enzyme expressed in polymorphonuclear cells infiltrating the ischemic brain, was performed. Infiltrating myeloperoxidase-positive cells are observed both in iNOS null mice and in controls (bottom panels). Scale bar (shown intop right panel in B): topand bottom panels, 50 μm; middle panel, 250 μm.
