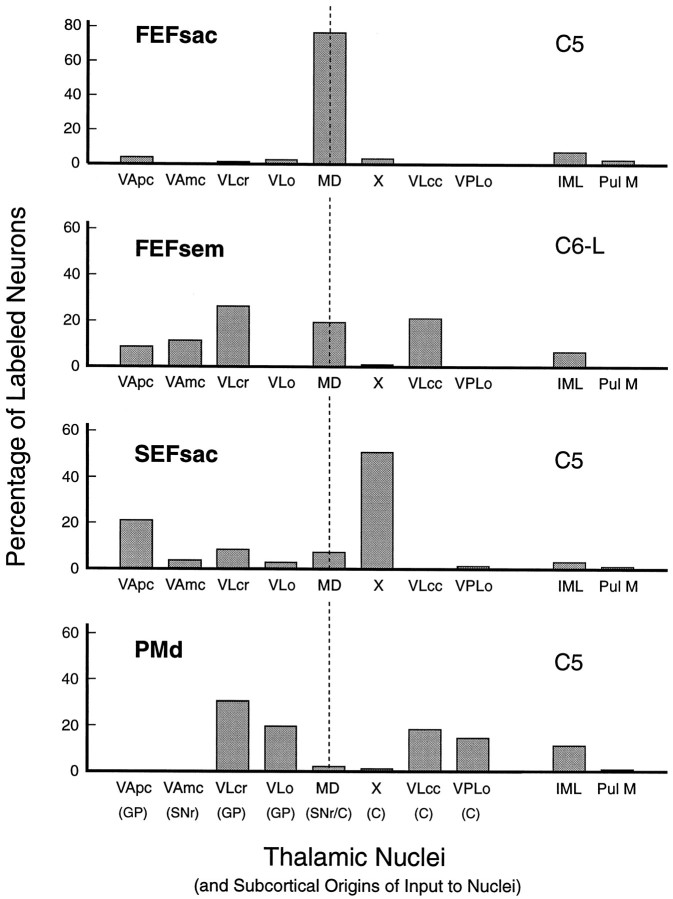
Fig. 8.
Quantitative comparison of distribution patterns of labeled neurons in thalamic nuclei from the four cortical injection sites. Labeled neurons were counted within the cytoarchitectural boundaries of 31 sections spaced at 250 μm intervals in monkeys C5 and C6. Each graph illustrates the percentage, in each nucleus, of the total number of neurons labeled by that particular injection. The thalamic nuclei are arranged on the x-axis so that regions that receive input from the internal segment of the globus pallidus and the pars reticulata of the substantia nigra are on theleft of the vertical dashed line and the nuclear regions that receive input from the cerebellar nuclei are on the right of the dashed line. The medial dorsal nucleus receives input from both the basal ganglia and the cerebellum. Intralaminar nuclei (Pcn and Cl), indicated byIML, and the Pul M are not included in the basal ganglia versus cerebellum distribution dichotomy. A total of 5692 neurons were labeled by the FEFsac injection, 2876 by the FEFsem injection, 460 by theSEFsac injection, and 1288 by the PMdinjection. C, Cerebellum, predominantly via the dentate nucleus; FEFsac, saccadic subregion of the frontal eye field; FEFsem, smooth eye movement subregion of the frontal eye field; GP, globus pallidus;IML, intralaminar nuclei; MD, medialis dorsalis; PMd, hand region of the dorsal premotor cortex; Pul M, pulvinaris medialis;SEFsac, saccadic subregion of the supplementary eye field; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticularis;VAmc, ventralis anterior, pars magnocellularis;VApc, ventralis anterior, pars parvocellularis;VLcc, caudal portion of ventralis lateralis, pars caudalis; VLcr, rostral portion of ventralis lateralis, pars caudalis; VLo, ventralis lateralis, pars oralis;VPLo, ventralis posterior lateralis, pars oralis;X, area X of ventral lateral complex.