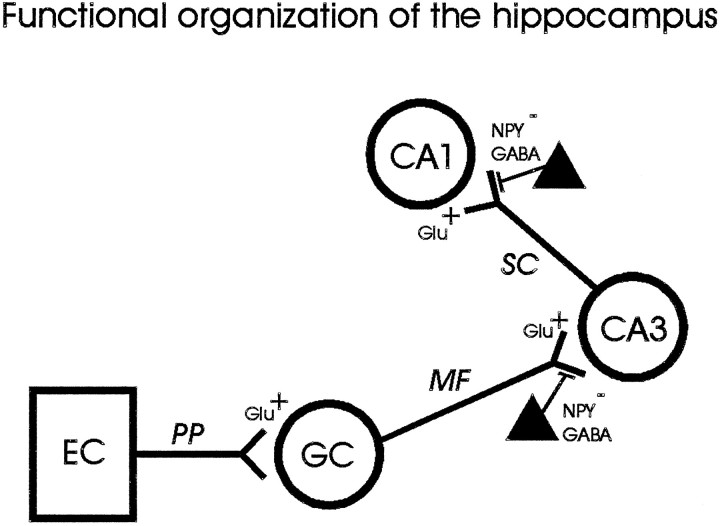
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the hippocampal trisynaptic circuit. Feed-forward excitation enters the hippocampus from the entorhinal cortex (EC) via the perforant path (PP); glutamatergic granule cells (GC) in the dentate gyrus make excitatory synaptic connections ontoCA3 pyramidal neurons via mossy fibers (MF); and glutamatergic CA3pyramidal neurons make excitatory synaptic connections ontoCA1 pyramidal neurons via the Schaffer collaterals (SC). Interneurons containing NPY and GABA (filled triangles) are thought to inhibit excitation by acting at presynaptic sites to reduce excitatory neurotransmitter release at mossy fiber–CA3 and Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in the hippocampus.