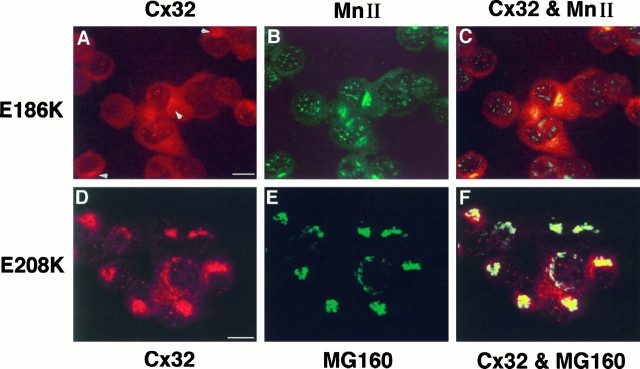
Fig. 4.
Localization of Cx32 mutantsE186K and E208K in PC12J cells by indirect immunofluorescence using scanning laser confocal microscopy.A–C, Cells expressing E186K (clone 414.10) were double-stained with the mouse monoclonal antibody 7C6.C7 against Cx32 (A; rhodamine) and a polyclonal antiserum against rat α-mannosidase II (MnII) (B; fluorescein).A and B are superimposed inC. D–F, Cells expressingE208K (clone 208.49) were double-stained with the polyclonal antiserum B1J against Cx32(D; rhodamine) and the monoclonal antibody 10A8 againstMG160 (E; fluorescein). Dand E are superimposed in F. The characteristically punctate staining of E186K obtained with 7C6.C7 (see Fig. 5; data not shown) is difficult to see because of high background staining contributed by the α-mannosidase II antibody; arrowheads are used to indicateCx32 immunoreactivity in the cytoplasm of these cells. Note the absence of Cx32 at the cell surface in these two mutants. Scale bars, 10 μm.