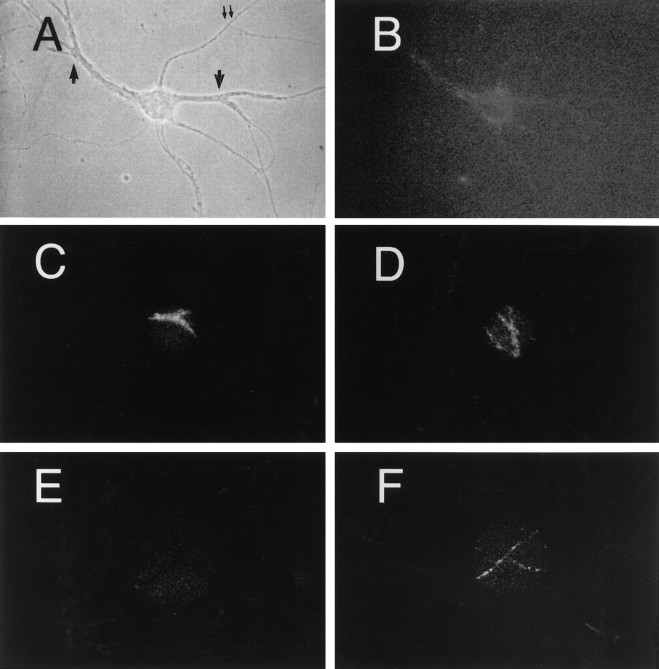
Fig. 2.
Dendritically uncaged FITC-Tf is later present in axons. Cells were incubated with 300 nm (caged)FITC-Tf for 30 min and then analyzed by video microscopy. A, Phase-contrast image of hippocampal neuron grown at low density.B, Excitation with FITC wavelength reveals only autofluorescence but no Tf-labeled structures [compare with thedots seen in fluorochrome (uncaged)-conjugated images of Figure 1]. The high background is caused by the increase in the camera sensitivity to permit the visualization of the cell. C, D, With the mercury light diaphragm closed to its maximum, two dendritic areas are uncaged by a 1 sec illumination with UV wavelength. Only the dendrites are exposed. The rest of the cell is invisible. Switching back to FITC wavelength reveals the presence of Tf-positive dots in the excited dendrites (arrows inA). E, Excitation of the axon of this cell (double arrows in A) with FITC wavelength immediately after dendritic UV uncaging reveals no emission.F, At 45 min after dendritic uncaging, several FITC-positive dots in the axon are evident.