Fig. 1.
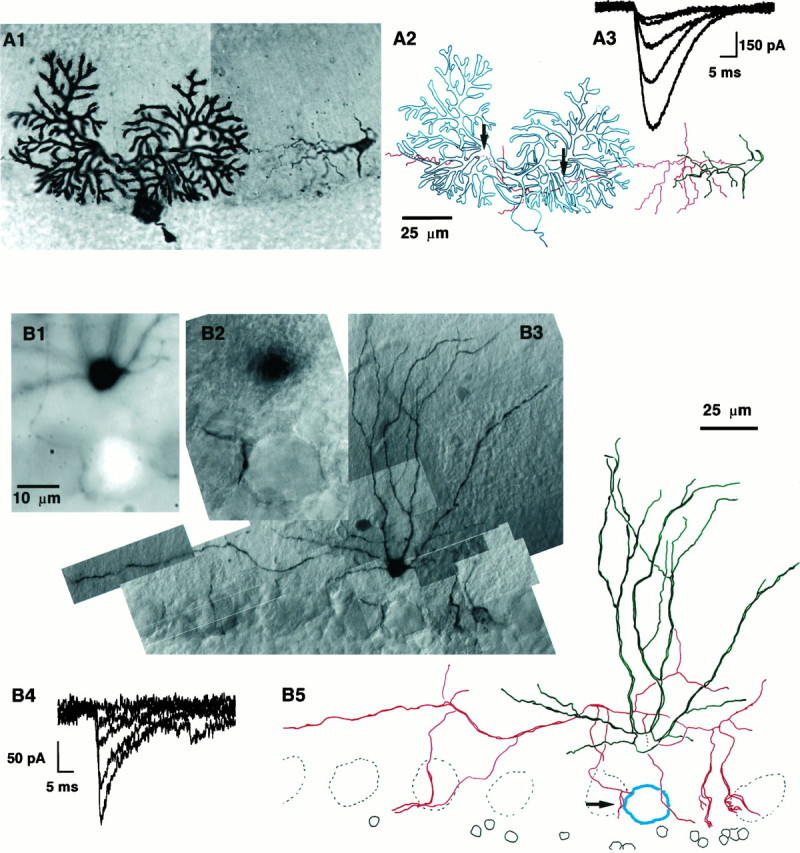
Illustration of the developmental decrease of sa-IPSC amplitude. The PC layer has been orientedhorizontally, the pial surface is toward thetop, and the granular layer is toward thebottom. A, BC–PC pair from a P11 rat.A1, Photo montage of the pair with both cells filled with biocytin. The PC is on the left, and the BC is on the right. The BC axon can be followed until it enters the PC dendritic field and can be seen again as it continues its course past the PC. The PC axon is cut shortly after its origin. The external germinal layer can be seen above the limit of the Purkinje cell dendritic field (top left corner). A2, Drawing of the pair; the somatodendritic compartment of the basket cell is drawn in green, and its axon is inred. The PC is drawn in blue. The twoarrows point to sites of putative synaptic contacts between the presynaptic axon and the postsynaptic cell. Note that the dendritic arborization of the BC is little developed at this stage, whereas its axon is already long and ramified but does not show any of the axosomatic specializations typical of BC–PC synapses. This pair was dehydrated and embedded in Canada balsam; during this procedure the slice shrunk with local inhomogeneities, which gave rise to the “wavy” appearance of the axon. The scale bar holds for bothA1 and A2. A3, Examples of sa-IPSCs recorded in the PC after short voltage pulses in the presynaptic BC. B, BC–PC pair from a P28 rat. The BC was filled with biocytin, and the soma of the PC was filled with Lucifer yellow. B1, Detailed picture of the pair taken with fluorescence microscopy. The soma of the PC is the bright spot at the bottom (the dendritic tree of the PC was not filled). The soma of the BC is the black spot at the top. The BC axon originates on theright of the cell body (at “3 o’clock”) and bends upward at the beginning of its course. Five out-of-focus dendritic branches of the BC are visible as well. A descending axon collateral of the BC comes in close apposition to the PC soma from the left. B2, Transmitted light picture of the same field as in B1. The soma of the PC is clearly recognizable (in focus) as well as the putative contact (on the left, at “9 o’clock”), the soma of the BC is slightly out of focus. The scale bar is common forB1 and B2. B3, General view of the BC (only two-thirds of the axon are shown). This slice was not dehydrated and was embedded in Tris buffer with 15% glycerol, leading to a better preservation of the neurite appearance than inA. B4, Examples of sa-IPSCs evoked in the PC on stimulation of the BC. Note the amplitude difference with the sa-IPSCs of A3. B5, Drawing of the pair. As in A, the somatodendritic compartment of the interneuron is green, the interneuron axon isred, and the postsynaptic PC is blue. Thearrow points to the putative synaptic contact. The dendritic arborization of the BC is much more extensive than inA2. The axon sends two thick descending collaterals toward PC somata on the right. The scale bar holds for both B3 and B5.
