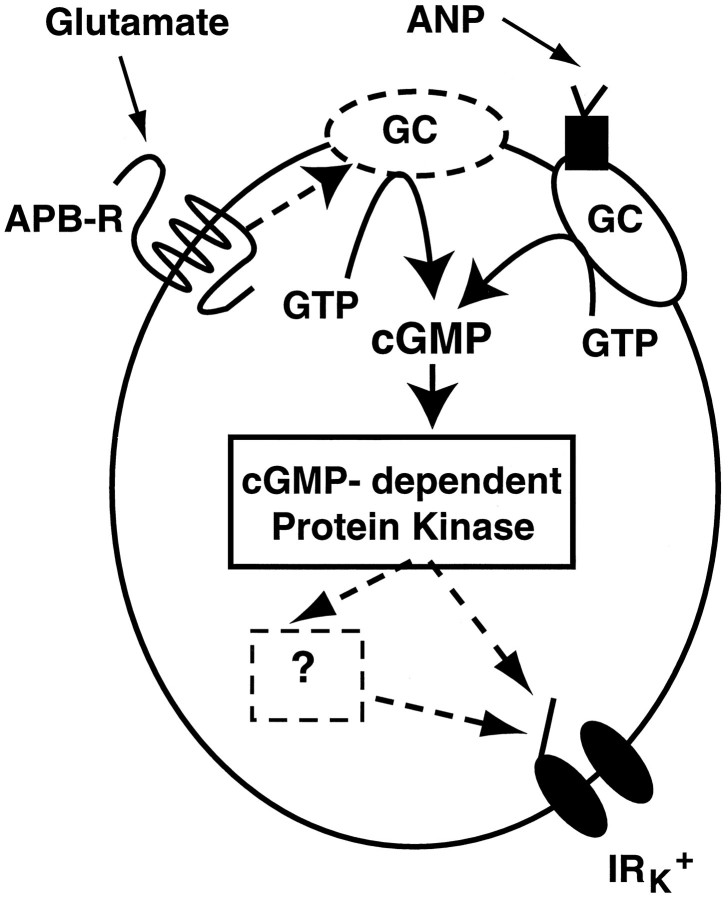
Fig. 7.
Model of glutamate-mediated IRK+ suppression. The simplest scheme consistent with the present data indicates that the APB receptor activates a membrane-bound guanylyl cyclase, thereby increasing intracellular cGMP. cGMP activates a protein kinase that may directly phosphorylate the IRK+ channel; however it is possible that one or more intermediaries is involved. Nevertheless, the result of increased cGMP is a closure of IRK+ channels. The dashed arrow and dashed border around GCsignify the hypothesized pathway by which the APB receptor upregulates the activity of a membrane-bound guanylyl cyclase. The dashed arrows between the kinase and the IRK+ channel signify that the site(s) of action of the kinase has not been established. The dashed box denotes one or more hypothetical intermediate steps, such as activation of a phosphatase, between the cGMP-dependent kinase and IRK+.