Fig. 1.
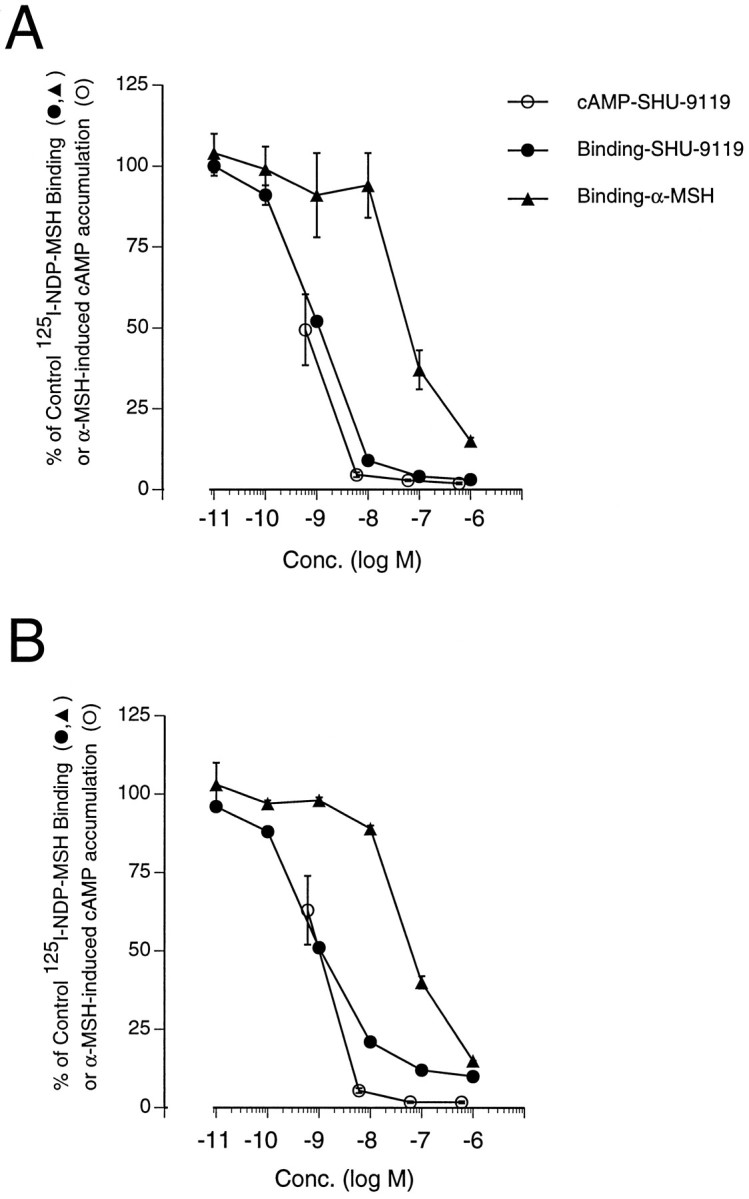
SHU-9119-mediated inhibition of α-MSH (10 nm)-induced cAMP accumulation (○) and specific [125I]-NDP-MSH binding (•) in B16-G4F cells stably expressing the rat MC3-R (A) or MC4-R (B). The potency of α-MSH in inhibiting [125I]-NDP-MSH binding is shown for comparison (▴). For cAMP, the stimulation by 10 nm α-MSH is defined as 100%, and the symbols indicate mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. For [125I]-NDP-MSH binding, control binding in the absence of SHU-9119 or α-MSH was defined as 100%, and the symbols indicate means of two to three separate experiments for SHU-9119 and of one experiment for α-MSH. Because of the different numbers of experiments shown in the various binding curves, their respective error terms are indicated separately.A, B16-G4F-rMC3. cAMP levels under basal and α-MSH-stimulated conditions were 2.2 ± 0.4 and 93.9 ± 36.8 pmol/well (mean ± SEM), respectively. SHU-9119 was tested alone for intrinsic agonism in one experiment at concentrations ranging between 6 × 10−11m and 6 × 10−7m, and all values were ≤ basal levels. Mean control [125I]-NDP-MSH binding ranged between 7142 ± 351 and 1680 ± 147 cpm/well (mean ± SD); the curve represents data pooled from three experiments.B, B16-G4F-rMC4. cAMP levels under basal and α-MSH-stimulated conditions were 0.9 ± 0.4 and 93.9 ± 24.1 pmol/well (mean ± SEM), respectively. SHU-9119 was tested alone for intrinsic agonism in one experiment at concentrations ranging between 6 × 10−11m and 6 × 10−7m, and all values were ≤ 2.8 ± 0.8 pmol/well (mean ± SD). Mean control [125I]-NDP-MSH binding ranged between 901 ± 51 and 1068 ± 169 cpm/well (mean ± SD); the curve represents means of data pooled from two experiments.
