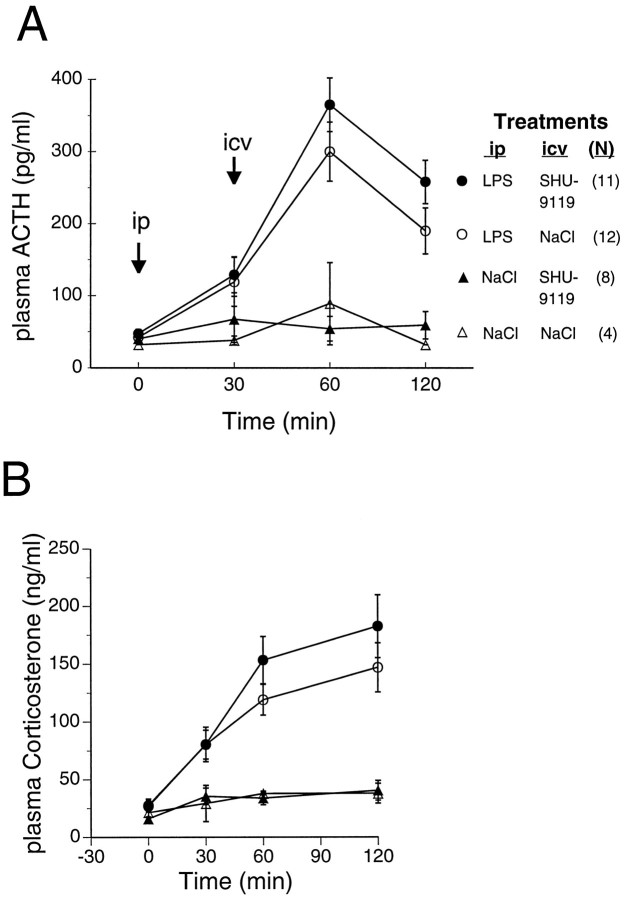
Fig. 6.
Lack of effect of centrally administered SHU-9119 on LPS-induced ACTH and CS secretion. Rats were treated with LPS (25 μg/kg, i.p.) or with saline injection vehicle at time 0, and received the indicated injectates intracerebroventricularly 30 min later.A, B, Time course of LPS-induced plasma ACTH (A) and CS (B) levels in the presence and absence of intracerebroventricular SHU-9119 (200 ng). Data fromA and B, respectively, were represented as area under the plasma hormone-time response curves (not shown) for statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA. For ACTH (A), significance of the main effect of LPS isF(1,31) = 64, p < 0.0001. For CS (B), significance of the main effect of LPS is F(1,31) = 30, p< 0.0001. Effect of SHU-9119 was not significant for either ACTH or CS. Data from a subset of the rats used in this experiment are also included in the study shown in Figure 4.