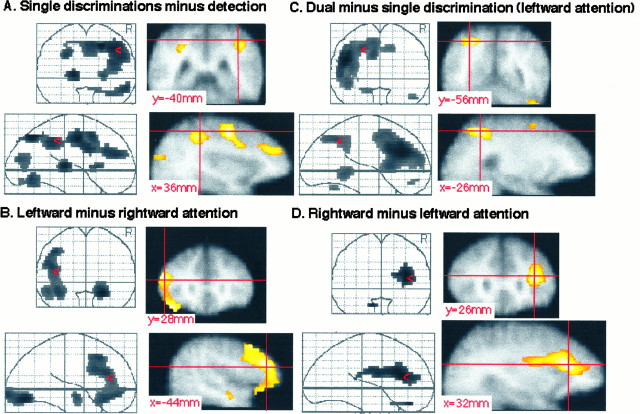
Fig. 3.
First experiment. All Z-maps are thresholded at p < 0.2. The right hemisphere is on the reader’s right hand in the coronal views. A, Subtraction of detection from the mean of all single discrimination conditions. Left top and bottom subquadrants, Coronal and sagittal see-through projections;right top subquadrant, coronal slice throughy = −40 mm; left bottom subquadrant, sagittal slice through x = 36 mm. The crosshair marks the right intraparietal sulcus.B, Subtraction of the right object from the left object single-feature discrimination conditions. Left top andbottom subquadrants, Coronal and sagittal see-through projections; right top subquadrant, coronal slice through y = 28 mm; left bottom subquadrant, sagittal slice through x = −44 mm. The crosshair marks the left lateral frontal activation. C, Subtraction of the mean of the single discriminations from the dual discrimination condition. Left top and bottom subquadrants, Coronal and sagittal see-through projections; right top subquadrant, coronal slice through y = −56 mm; right bottom subquadrant, sagittal slice throughx = −26 mm. The crosshair marks the left superior parietal lobule. D, Subtraction of the left object from the right object single-feature discriminations.Left top and bottom subquadrants, Coronal and sagittal see-through projections; right top subquadrant, coronal slice through y = 26 mm; right bottom subquadrant, sagittal slice throughx = 32 mm. The crosshair marks the right lateral frontal activation.