Fig. 1.
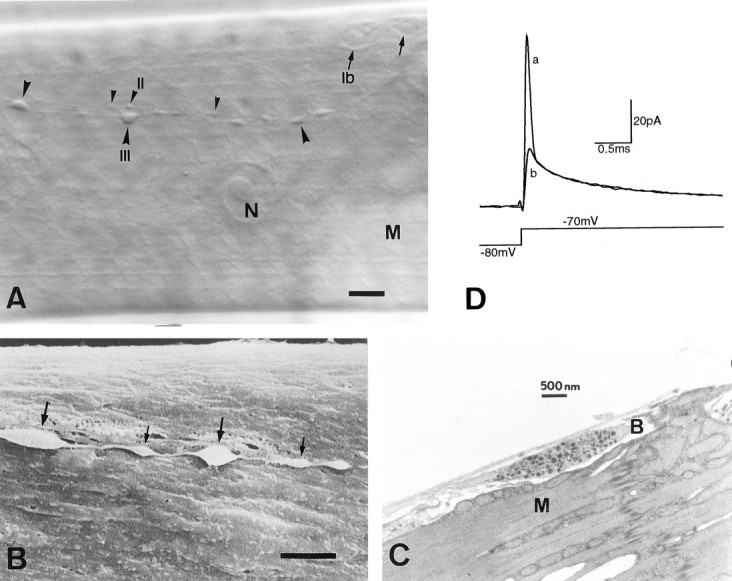
Type III synaptic boutons onecd1 larval muscle fiber 12.A, Nomarski view showing type Ib(arrows), type II (small arrowheads), and type III (large arrowheads) synaptic boutons after collagenase treatment.B, Scanning electronmicrograph of type III boutons. Notice the presence of relatively large (thick arrows) and small (thin arrows) boutons within the same axon string, and also their superficial location and accessible membrane.C, Transmission electronmicrograph from a wild type, showing a single type III bouton with a mixed population of dense-core vesicles. Note the elongated shape and the virtual absence of subsynaptic reticulum around the bouton. N, Nucleus;M, muscle fiber; B, synaptic bouton. Scale bar: A, 10 μm; B, 3 μm.D, Synaptic bouton capacitive current before (a) and after (b) electronic compensation of the first exponential component, in response to a voltage depolarization that elicits passive membrane currents only. The first exponential corresponds to the capacitance of the boutons under the recording pipette. Each trace represents the average of 20 current records.
