Fig. 3.
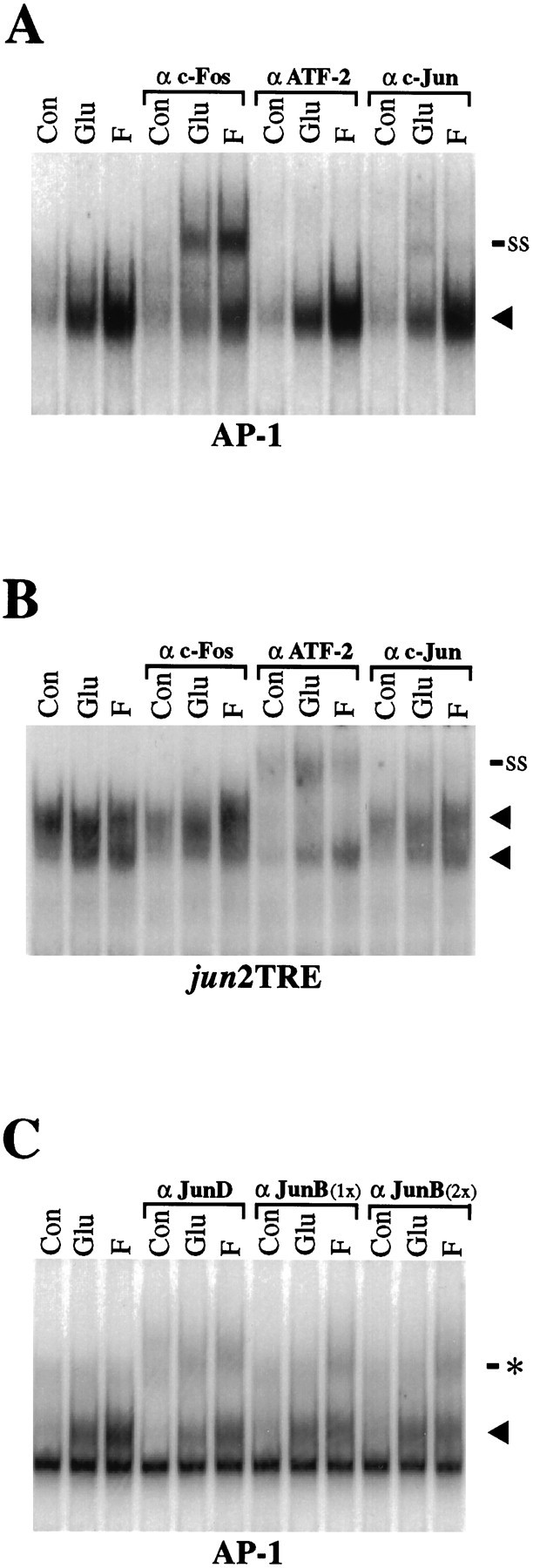
Supershift analysis of AP-1 and jun2TRE binding complexes after glutamate and forskolin stimulation.A, After 2 hr of glutamate (Glu) and forskolin (F) stimulation, AP-1-binding activity is increased over control (Con, no drug treatment), as indicated by the increased intensity of the specific complex (arrowhead). Addition of anti-Fos antibodies (α c-Fos) results in the appearance of a supershifted band (ss), indicating that Fos protein is present in the glutamate- and forskolin-induced AP-1-binding complex. The ATF-2 antibody (α ATF) has no effect on AP-1 binding. The c-Jun antibody (α c-Jun) results in a reduction in the overall levels of AP-1 binding, suggesting that addition of the antibody is interfering with formation of the DNA/protein complex. In addition, a minor supershifted band is observable after glutamate and, to a lesser extent, after forskolin stimulation. B, In contrast to AP-1 binding (A), protein binding to the jun2TRE after 2 hr of glutamate and forskolin stimulation can be supershifted by addition of ATF-2 antibodies, but not by addition of c-Fos antibodies.Arrowheads indicate two specific protein–oligonucleotide complexes. A modest reduction injun2TRE binding and a minor supershifted band are also seen after addition of c-Jun antibodies. C, Binding to the AP-1 element can be disrupted by addition of either a JunD (αJunD) or a JunB (α JunB) antibody. Addition of the JunD antibody reduces basal binding as well as glutamate- and forskolin-induced binding. The antibody directed against JunB selectively reduces the forskolin-induced binding complex. No difference is apparent if 1 μg (1×) or 2 μg (2×) of JunB antibody is included per lane. These reductions in the induced specific complexes (arrowhead) are associated with the appearance of modest probable supershift bands (asterisk). The SP AP-1 and hMT AP-1 oligonucleotides were used in A andC, respectively. A nonspecific binding complex is apparent below the specific band in C (not present inA) and is attributable to flanking sequences of the hMT probe, which are distinct from those of the SP probe (see Materials and Methods). Each experiment is representative and was performed at least four times (A, B) or twice (C).
