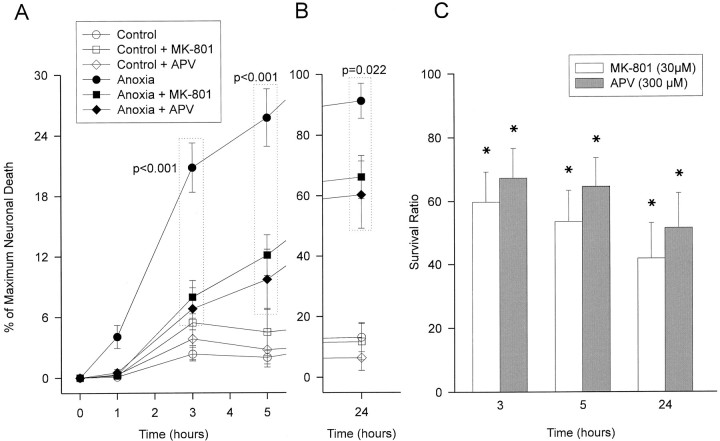
Fig. 3.
OGD-induced neuronal injury is partially mediated by NMDA receptor activation. Slice cultures were exposed to 60 min OGD alone (11 slices) or in the presence of 30 μm MK-801 (11 slices) or 300 μmdl-APV (9 slices). Antagonists were present from 15 min before OGD until the end of the 24 hr period. A, B, Representative series of experiments. Both antagonists equally reduced anoxic injury when compared with untreated anoxic slices (ANOVA followed by the Newman–Keuls procedure for multiple comparisons; groups included are in dotted boxes, p values marked on plot). Open symbols, Glucose deprivation in the presence of 2 mm 2DG without anoxia (no treatment, 11 slices; MK-801, 11 slices; APV, 13 slices). A, Time course of neuronal cell death at 0–5 hr. B, Extent of neuronal death at 24 hr (note differences in ordinate between A andB). C, Effect of NMDA antagonists on the survival of OGD-challenged neurons over 24 hr. Data were pooled from two series of experiments using MK-801 (22 total slices) and APV (23 slices). Protective efficacy of a treatment was expressed as a survival ratio, defined as 100 × (1 −Dtreated/Duntreated), whereDtreated/Duntreatedis the ratio of OGD-induced neuronal death in the antagonist treated and untreated groups, respectively. A value of 100 indicates that the treatment completely prevented neuronal death, whereas 0 indicates no effect of treatment. Asterisks indicate significant differences from zero.