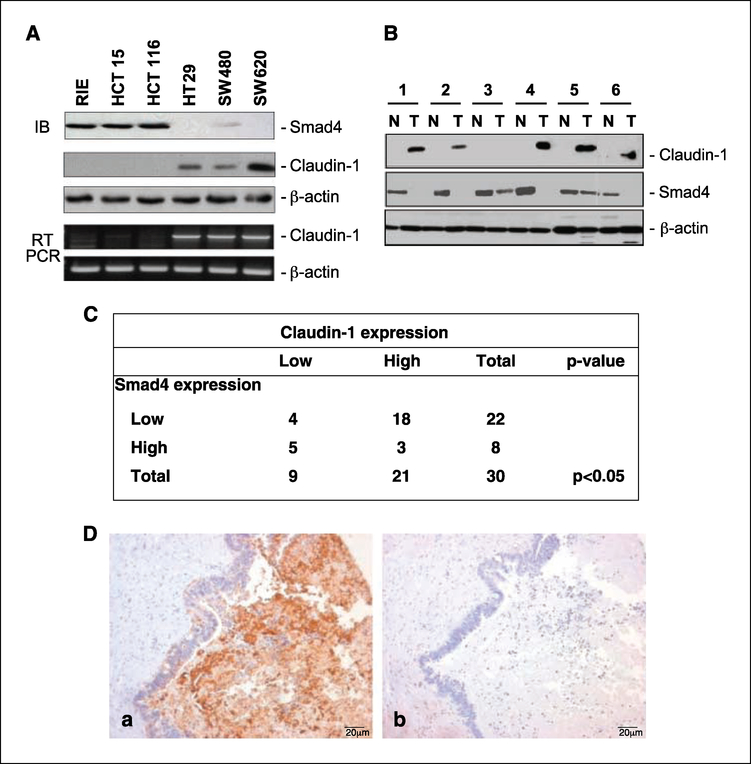
Figure 1.
Inverse Smad4 and claudin-1 protein expression in matched human colorectal carcinoma samples and cell lines. A, protein lysates and total RNA from the indicated cell lines were obtained as described in Materials and Methods and subjected to immunoblotting (IB) and semiquantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) for claudin-1, Smad4, and β-actin. B, the tissue samples were obtained from six patients with colon cancer; N, normal mucosa; T,primary colon cancer. Protein lysates were prepared from tissues homogenized in a lysis buffer followed with clearance by centrifugation. Equal amounts of lysates were used in immunoblotting assays for claudin-1 and Smad4. Same blots were stripped and reprobed with β-actin to assess equal protein loading. C, correlation between claudin-1 and Smad4 expressions in colon cancer. Data from custom colorectal cancer tissue arrays (tissue microarrays developed at Vanderbilt) that contain surgical specimens from 30 primary and paired metastatic fresβ-frozen human colorectal cancer samples are shown. A significant inverse correlation between claudin-1 and Smad4 expression was observed (P < 0.05) using χ2 approximation in metastatic patient samples. The staining was designated low or high based on staining intensity and the number of cells stained. D, representative staining for claudin-1 (a) and Smad4 (b) for a metastatic patient sample. Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin to determine the structural details.