Fig. 2.
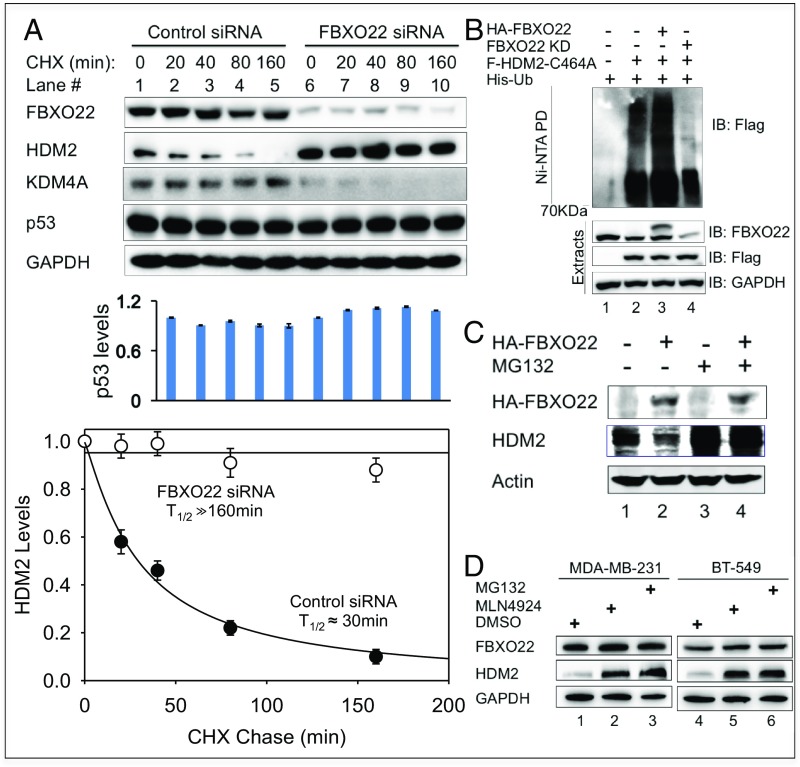
FBXO22 targets cellular HDM2 for degradation. (A) Depletion of FBXO22 results in prolonged t1/2 of HDM2 in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cycloheximide assays were performed to measure HDM2 decay rates in cells treated with control or FBXO22 KD siRNA. Graphs represent an average of three independent experiments (biological replicates), with error bars indicating SD. Graphing and calculation of t1/2 were done by using the scientific data analysis and graphing software SigmaPlot. (B) FBXO22 is critical for cellular ubiquitination of HDM2. MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with the His-ubiquitin expression vector and various combinations of HA-FBXO22 and Flag-HDM2 C464A in the presence or absence of anti-FBXO22 siRNA as indicated. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were treated with MG132 (10 μM) for 6 h to block protein degradation. His-ubiquitin–modified proteins were isolated and purified under denaturing conditions as described in SI Appendix, Methods. Anti-Flag Western detects Flag-HDM2 C464A modified by His-ubiquitin. (C) Forced expression of FBXO22 decreased the protein level of HDM2 in a manner that depends on proteasomal activity. HeLa cells were transfected with a vector expressing HA-FBXO22, and, before lysis, the cells were treated with MG132 (10 μM) for 6 h. The levels of the indicated proteins were determined by immunoblot analysis. (D) Stabilization of HDM2 by MLN4924. MDA-MB-231 or BT-549 cells were treated with DMSO, MLN4924 (3 µM), or MG132 (10 µM) for 24 h, followed by immunoblot analysis.