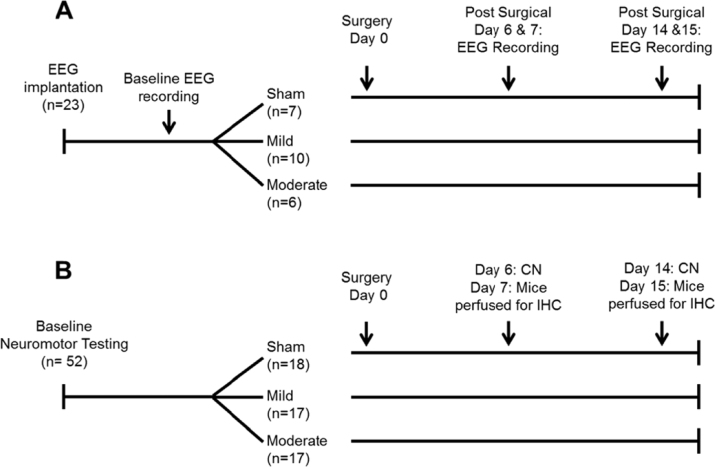
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the protocols used in Experiments 1, 2 and 3. (A) In Experiment 1, 48 h baseline electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings were obtained from undisturbed mice. Mice were then randomized into one of three surgical conditions: control (sham) surgeries; mild traumatic brain injury (TBI; 0.5 mm controlled cortical impact depth); moderate TBI (1.0 mm controlled cortical impact depth). Recordings of the EEG were obtained from the same animals one and two weeks post-surgery. (B) Animals in Experiments 2 and 3 were used to determine the impact of TBI on neuromotor function (CN: composite neuroscore; Experiment 2) and to provide brain tissue for immunohistochemical assessment of TBI effects on selected neurotransmitters (Experiment 3). After baseline neuromotor testing, animals were randomized into either a sham surgical group (control), mild TBI group or moderate TBI group as in Experiment 1. Composite neuroscores were obtained one and two weeks post-surgery. After each neuromotor testing session, a subset of mice was sacrificed and brains removed for immunohistochemistry (IHC).