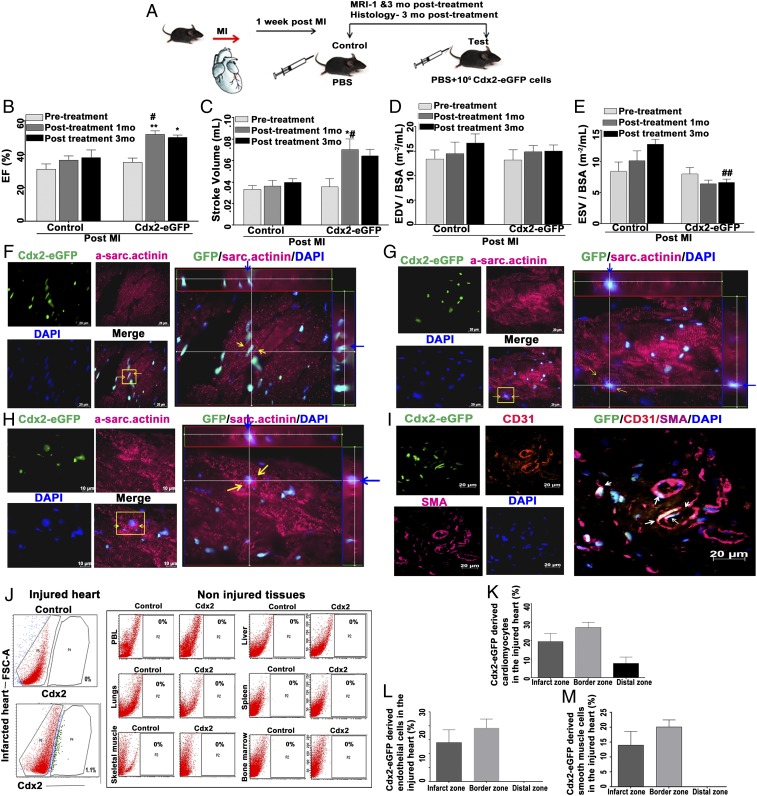
Fig. 6.
Cdx2-eGFP cells contributed to cardiac repair in vivo. (A) Schema illustrating MI induction and Cdx2 cell delivery in vivo. (B) Cardiac MRI analyses showing a significant increase in EF in Cdx2 cell-injected mice versus the control animals at 1-mo and 3-mo time points compared with the pretreatment timeline (Cdx2 group, n = 8; control) group, n = 5). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. #P = 0.0263 (control vs. test at 1 mo), **P = 0.0095 (test before treatment vs. test at 1 mo post-MI and *P = 0.0269 test 3 mo post-MI). (C–E) Left ventricular functional parameters, including SV, LVEDV, and LVESV, as measured in control and cell-treated groups showed a reduction in adverse remodeling. (C) SV is significantly higher in the test group at 1 mo versus the control group at 1 mo post-MI (#P < 0.05). SV within the test cohort before treatment and after Cdx2-eGFP cell injection: before treatment test vs. test at 1 mo post-MI (*P = 0.0121). (D) LVEDV indexed to bovine serum albumin (BSA) did not show significant change in control and test mice at any time point. (E) Cdx2-eGFP cell delivery significantly reduced ESV compared with the control mice at 3 mo post-MI (##P = 0.00045). (F–H) Cdx2-eGFP cells “homed” to injured heart and differentiated into CMs in vivo. CMs expressing α-sarcomeric actinin derived from Cdx2-eGFP cells in the border zone are shown. The panels show striated CMs with nuclear eGFP [Alexa 647, pink; nuclei, blue (DAPI)]. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (Right) Yellow arrows indicate Cdx2-derived CMs highlighted in the Z-stack view. Blue arrows indicate the same highlighted cell within the Z-stacks, demonstrating nuclear eGFP signal within an α-sarcomeric actinin+ cell (Movies S12–S14). (I) Cdx2-eGFP cells contributed to blood vessel formation in vivo. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (Right) Border zone shows CD31+ SMA+ cells with nuclear eGFP incorporated into blood vessels highlighted with white arrows. (J) Flow cytometry analysis revealed that the homing and retention of Cdx2-eGFP cells are specific to the injured myocardium and not to any noninjured organs. Quantification of the percentage of Cdx2-eGFP–derived CMs (K) and vascular cells (L and M) is shown in heart sections in vivo in the infarct zone, border zone, and distal zone, demonstrating differentiation into cardiovascular lineages. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.