Figure 1.
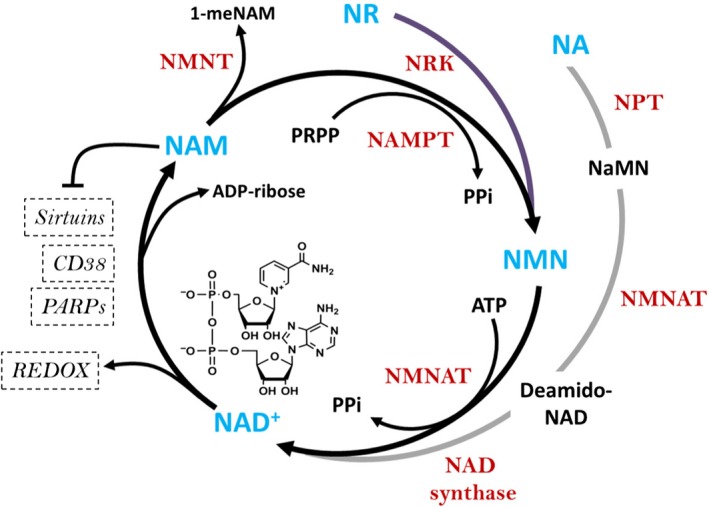
NAD+ salvage pathway in mammals. NAM is the major NAD+ precursor in mammals. NA and NR can also be used to synthesize NAD+. NAMPT is the rate‐limiting step for the synthesis of NAD+ from NAM. Once NMN from NR and NAM or deamido‐NAD from NA are formed, it is converted to NAD+ by the action of NMNAT or NAD synthetase, respectively. The NAD+ generated can then be used for cellular redox reactions or as substrate for the activity of PARPs and sirtuins. NA, nicotinic acid; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NAMPT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NAM, nicotinamide; NR, nicotinamide riboside; NRK, nicotinamide riboside kinase; NPT, nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NMNAT, NMN adenylyltransferase; NNMT, nicotinamide‐N‐methyltransferase; NaMN, nicotinic acid mononucleotide; PRPP, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; PPi, inorganic pyrophosphate; PARPs, poly‐ADP ribose polymerases.
