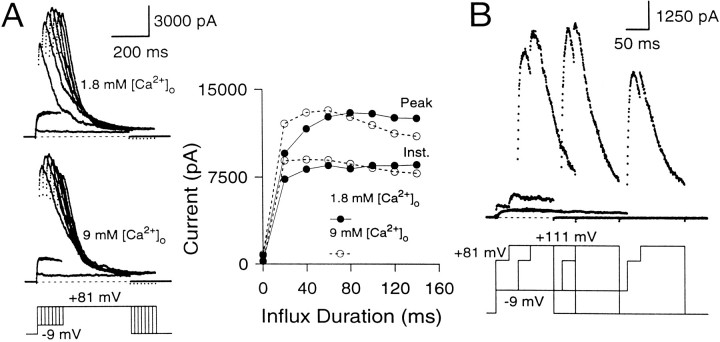
Fig. 6.
The maximal peak current elicited at +81 mV with long Ca2+ influx steps defines the maximal available BK conductance. A, The cell was stepped from the holding potential (−69 mV) to −9 mV to produce Ca2+ influx and then stepped to +81 mV. Thetop traces show currents elicited in external saline containing 1.8 mm[Ca2+]o, whereas thebottom traces show currents in the same cell in external saline containing 9 mm[Ca2+]o. On theright, the instantaneous and peak currents are plotted against the duration of the influx step. In both salines, the maximal peak currents at +81 mV reach the same amplitude. Perforated-patch method. Rs, 15.5 MΩ;Cm, 7.8 pF; 80% compensated. B, The cell was stepped to −9 mV for varying durations to produce Ca2+ influx and then stepped to +81 mV for 50 msec to activate the BK current robustly. After 50 msec at +81 mV, the cell was stepped to +111 mV to detect the extent of BK current activation at +81 mV. External Na+ was replaced with N-methyl-d-glucamine (NMG) to circumvent the effects of intracellular Na+ block of BK channels at positive voltages (Yellen, 1984; see Materials and Methods). After short Ca2+ loading steps, there is some additional activation of BK current at +111 mV beyond what is seen at +81 mV. However, after Ca2+ influx steps of 150 msec and longer, additional activation at +111 mV does not occur, indicating that maximal activation of BK current has been achieved at +81 mV. Perforated-patch method.Rs, 11 MΩ;Cm, 4.5 pF; 80% compensated. Sampling period, 500 μsec.