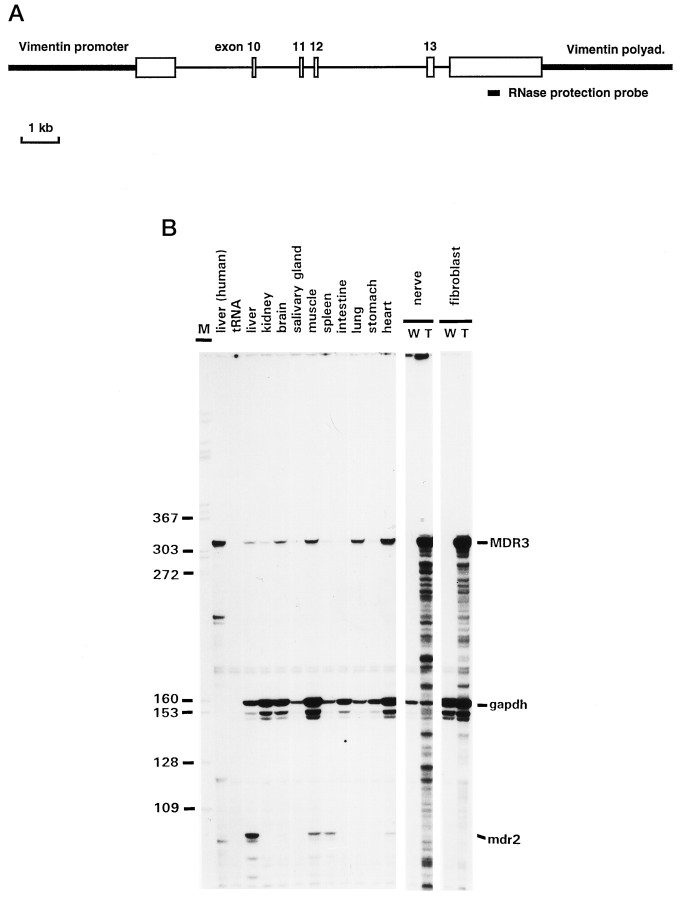
Fig. 1.
A, Schematic representation of the mini-gene construct used to generate MDR3 transgenic mice. White boxes represent parts of theMDR3 cDNA; intron sequences of the MDR3 gene are indicated by thin lines. TheMDR3 mini-gene is under the control of the hamstervimentin promoter and polyadenylation signal (thick lines). B, MDR3 mRNA levels in transgenic tissues. Total RNA was isolated from all major tissues and sciatic nerves of a V01 animal and analyzed by RNase protection. RNA isolated from transgenic (T) nerves and fibroblasts was compared with RNA isolated from wild-type (W) mice. The position of theMDR3-specific RNase protection probe is shown inA. The protected fragments representingMDR3, mdr2, and gapdh mRNA are indicated on the right. Because of the partial sequence homology of the MDR3-specific RNA probe with mouse mdr2 sequences, smaller fragments that representmdr2 mRNA were detected in RNA from liver, muscle, heart, and spleen. The expression pattern of this mdr2 mRNA is consistent with previous results (Croop et al., 1989; Teeter et al., 1990). An end-labeled DdeI digest of M13mp19 DNA was used as size marker (M); relevant sizes are indicated at the left.