Fig. 6.
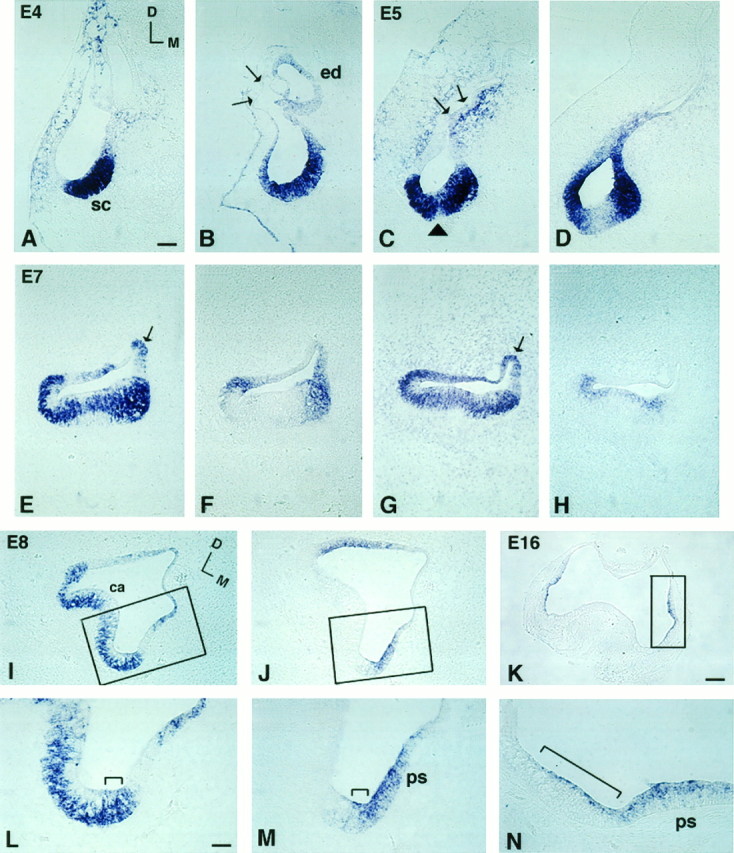
Comparison of BMP4 and BMP7 gene expression patterns in superior crista ampullaris from E4 to E16. Aand B, C and D,E and F, G andH, and I and J are pairs of adjacent 12 μm sections. Sections shown in A, C, E, G, and I were probed for BMP4; B, D, F, J, and K were probed for BMP7; andH was probed for BDNF. A andB were sections from stage 24 (E4) embryos;C and D from E5; E–H from E7; I, J, L, M from E8; and K, N from E16. At E4, (A) BMP4- and (B) BMP7-positive areas overlapped in the presumptive crista (sc). Arrows in B point to the thin epithelium at the dorsolateral portion of the otocyst that was negative for BMP7. By E5, BMP7 (D) has begun to segregate from the presumptive sensory area. Arrowheadin C points to the cruciatum that was negative for BMP4. The arrow points to the part of the otic epithelium with weak BMP4 expression next to the strong expression in the surrounding mesenchyme. This weak epithelial signal became the positive signal in the roof of the ampulla by E7 (arrow inE, G). At E7, BMP7 expression was restricted mostly to the nonsensory portion of the ampulla (F). On the other hand, the BMP4-positive area within the crista concentrated in supporting cells (E, G) rather than in hair cells, as contrasted by the pattern of BDNF expression (H). The areas within therectangles in I, J, and Kare enlarged in L, M, and N, respectively. BMP4 transcripts spanned the entire epithelium in one area of the ampulla (bracket in L), and this area was also positive for BMP7 (bracket inM). By E16, positive hybridization was found in the planum semilunatum (ps) and the crista ampullaris (bracket in N). Orientation: D, dorsal; M, medial. Refer to orientation axis in A for B–H and orientation axis in I for J–N.ca, Crista ampullaris; ed, endolymphatic apparatus; sc, superior crista; ps, planum semilunatum. Scale bars: A–J, 100 μm;K, 200 μm; L–N, 25 μm.
