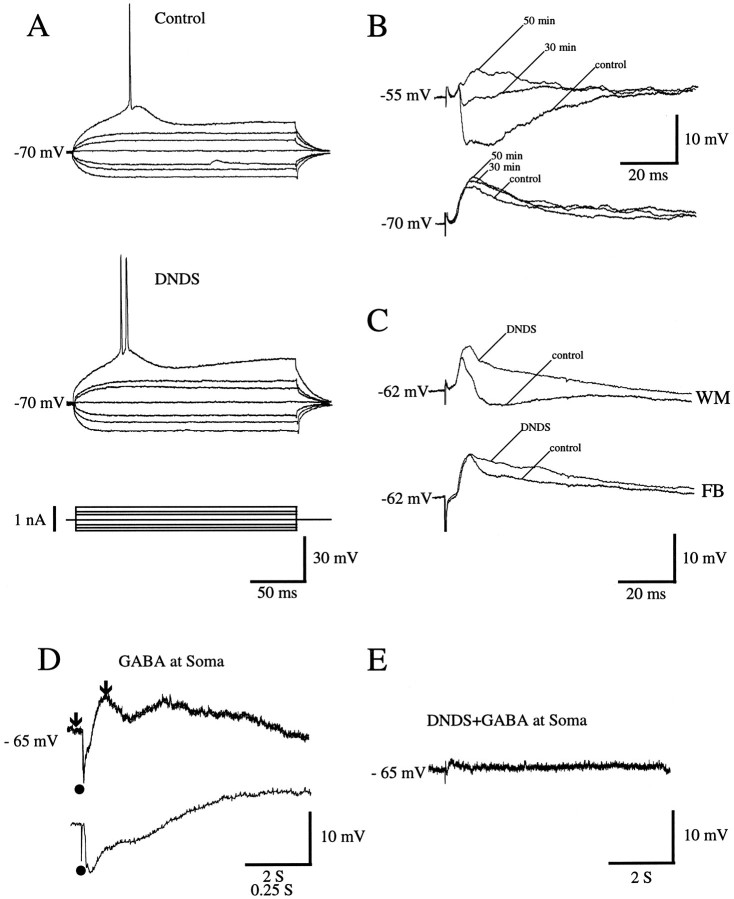
Fig. 6.
A–C, Intracellular blockade of IPSPs by DNDS in regular-spiking neurons of rat visual cortex.A, Response of layer 2/3 neuron in area 17 to injection of hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current. Control records were obtained immediately after impalement; records in the presence of DNDS were obtained 30 min later. Note that intracellular injection of DNDS has no significant effect on input resistance or membrane time constant. B, PSPs (recordings at different membrane potentials) of layer 2/3 neuron in area LM evoked by stimulation (1.6T) of forward input. Control trace was obtained immediately after impalement with DNDS-filled electrode. As DNDS slowly enters the cell, IPSP amplitude is reduced markedly 30 min after impalement and disappears altogether at 50 min. C, PSPs of layer 2/3 cell in area 17 after stimulation (1.7T) of inputs from white matter (WM) and feedback (FB) connections. Control traces represent recordings before intracellular infusion of DNDS. Traces labeledDNDS show responses 45 min after impalement and after DNDS effectively blocks IPSPs. D, Intracellular infusion of DNDS blocks response to local application of GABA. Intracellular response to GABA application (filled circle) near soma of layer 2/3 neuron in area 17 shortly after impalement with DNDS-filled electrode (top). The initial phase of the response (indicated by arrows) is shown at expanded time scale (bottom). E, Response to GABA application in the same neuron 30 min after impalement and infusion of DNDS.