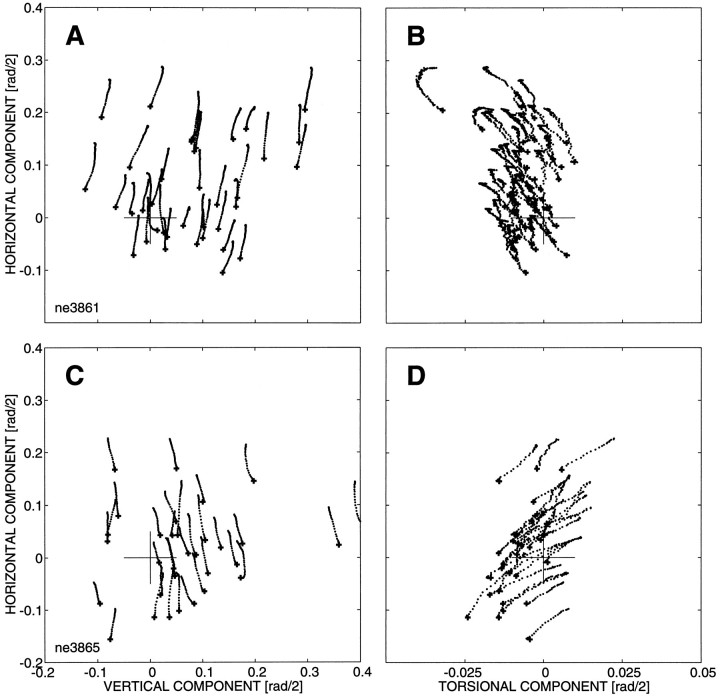
Fig. 5.
Results of electrical microstimulation at two different depths in the left cNRTP of monkey NE. Stimulation parameters: current strength, 50 μA; frequency, 330 Hz; train duration, 70 msec. Evoked eye movements were leftward, and at both sites movement direction and amplitude varied with initial eye position. A, C, Projection of the eye movement trajectories in Listing’s plane [the (y, z) plane];B and D present the same data in the (x, z) plane (see Tweed and Vilis, 1988; Van Opstal et al., 1991; Hepp et al., 1993). Note different scales. Top panels show data obtained at site 1, and the bottom panels represent site 2, which was located 500 μm deeper along the same penetration. Note that evoked eye movements at both sites have a substantial torsional displacement (B, D). However, the sign of the torsional movements is opposite for the two sites: movements at site 1 had a negative torsional displacement, whereas the gaze shifts evoked at site 2 had positive torsion. The size of the torsional displacement was independent of initial eye position (site 1: offset −0.006 rad/2; slope 0.009; r = 0.33;N = 42; p = 0.03; site 2: offset +0.013 rad/2; slope 0.013; r = 0.26; N = 42;p = 0.10) [see Van Opstal et al. (1991) and Hepp et al. (1993) for details on this procedure]. Note also the small negative torsional offset at the first stimulation site, which is absent at the second site.