Fig. 6.
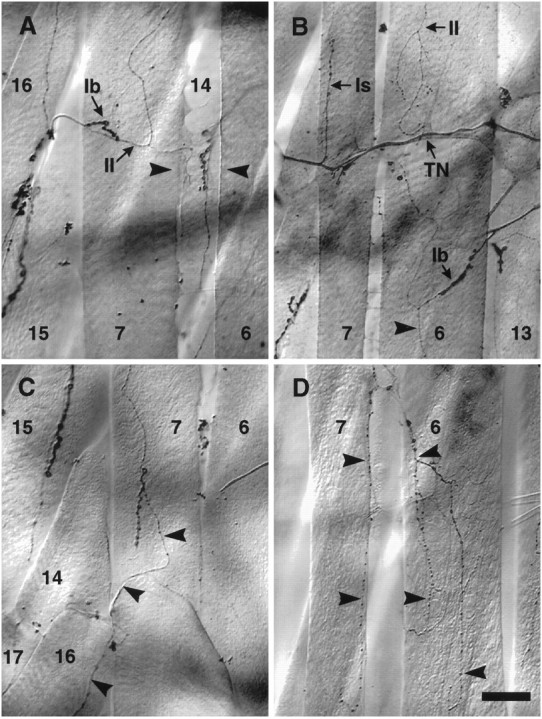
Collateral inputs are formed on denervated muscle fibers from nearby motor axons and terminals. A, An example of collateral inputs from the muscle15/16 cleft innervating muscle fiber7 from the medial aspect. Both type Iband type II endings are present.Arrowheads indicate the denervated cleft between muscle fibers 7 and 6. The inputs visible between the arrowheads are on the underlying muscle fiber 14. B, The three different types of ending morphology are evident in this example: an Isending from the transverse nerve (TN) to the posterior end of the anterior muscle fiber 7, a Ibinput from SNb branching onto the lateral edge of muscle fiber6, and two type II inputs: one arising laterally from SNb onto the anterior muscle fiber 6(source not shown), and the other laterally from SNb onto muscle fiber6 (arrowhead). C, A type II input from the next posterior 15/16cleft (arrowhead). Also visible are type Ib boutons that appear to be from the same source (see Fig. 7A).D, An example of a large, branched type II input from the 7/6 cleft ramifying over both muscle fibers 7 and 6(arrowheads). In contrast, type II inputs at the cleft in control animals are rare and small (see Results). Scale bar:A, C, D, 30 μm; B, 50 μm.
