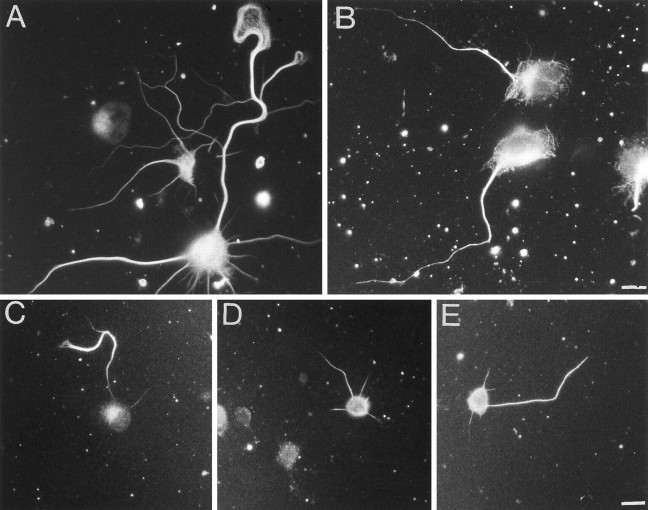
Fig. 5.
Effect of colchicine on tau binding in hippocampal neurons. A, Distribution of microtubules in hippocampal neurons, which have been treated with carrier (0.1% ethanol) only. Note that the microtubules seem to be distributed uniformly in the axonal shaft and that they extend far into the axonal growth cone.B, Distribution of microtubules in colchicine-treated (0.5 μm, 3 hr) hippocampal neurons. Note the decrease of the microtubule concentration toward the distal axon and the complete loss of growth cone microtubules. C–E, Distribution of tau in control cells (C) and cells treated with 0.5 (D) and 1 μm (E) colchicine. Note the redistribution of tau after colchicine treatment, resulting in a loss of the proximal-to-distal tau gradient. After 3 d in culture, colchicine at the indicated concentrations or, as a control, carrier only (0.1% final ethanol concentration) was added to the cultures. Cells were incubated for an additional 3 hr and then extracted and fixed as described in Materials and Methods. Tau-specific staining was obtained by monoclonal anti-tau antibody (Tau-1), and microtubules were stained with monoclonal anti-α-tubulin antibody (DM1A). Scale bars: 10 μm (A, B); 20 μm (C–E).