Fig. 7.
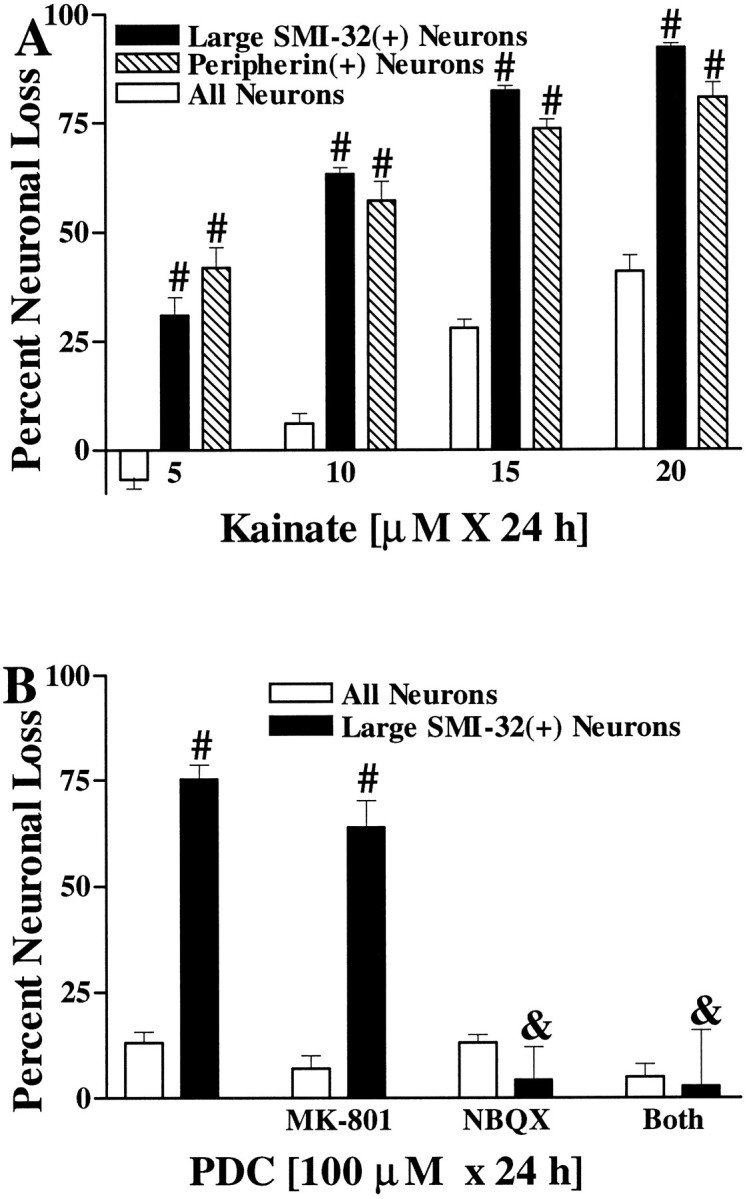
Motor neurons are selectively vulnerable to slow, excitotoxic injury. A, Large SMI-32(+) neurons and peripherin(+) neurons are selectively damaged by chronic kainate exposures. Cultures were exposed to the indicated kainate concentration for 20–24 hr, followed by evaluation of injury to the overall neuronal population and to the labeled neuronal population. Values represent mean ± SEM compiled from three to four representative experiments;n = 10–12 cultures per condition. # indicates labeled neuronal loss significantly different from total neuronal loss after the same exposure (p < 0.01 by two-tailedt test). B, Large SMI-32(+) neurons are selectively damaged by chronic exposure to the glutamate reuptake blocker PDC. Cultures were exposed for 24 hr to PDC (100 μm) alone or with the addition of glutamate receptor antagonists as indicated (each at 10 μm), followed by evaluation of damage to the overall neuronal population and to large SMI-32(+) neurons. Values represent mean ± SEM compiled from three to four representative experiments; n = 9–12 cultures per condition.# indicates large SMI-32(+) neuronal loss significantly different from total neuronal loss after the same exposure (p < 0.01 by two-tailed t test).& indicates large SMI-32(+) neuronal loss significantly different from that obtained in the 100 μm PDC condition (p < 0.01 by two-tailed ttest).
