Fig. 5.
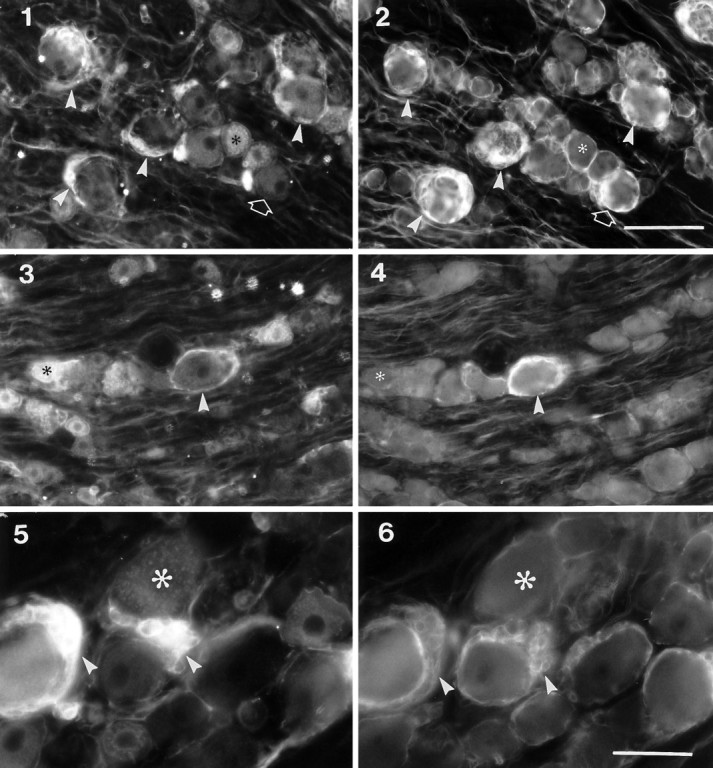
Colocalization of p75-ir with GFAP-ir in the ipsilateral (panels 1, 2, 5,6) and contralateral (panels 3, 4) L5 DRG after sciatic nerve transection. Panels 1,3, and 5 are sections stained with mouse antibodies to p75 followed by AMCA-conjugated secondary antibodies, andpanels 2, 4, and 6 are the same sections stained with rabbit antibodies to GFAP followed by FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies. Asterisks indicate neurons immunoreactive for p75 but negative for GFAP-ir;arrowheads in 1–4 indicate large neurons with p75-ir ring structures that were also immunoreactive for GFAP;arrowheads in 5 and 6 indicate clusters of glial cells that are both p75-ir and GFAP-ir; openarrows in 1 and 2 indicate a small neuron without p75-ir ring structure but with GFAP-ir. Scale bars:1–4 (shown in 2), 100 μm; 5,6 (shown in 6), 50 μm.
