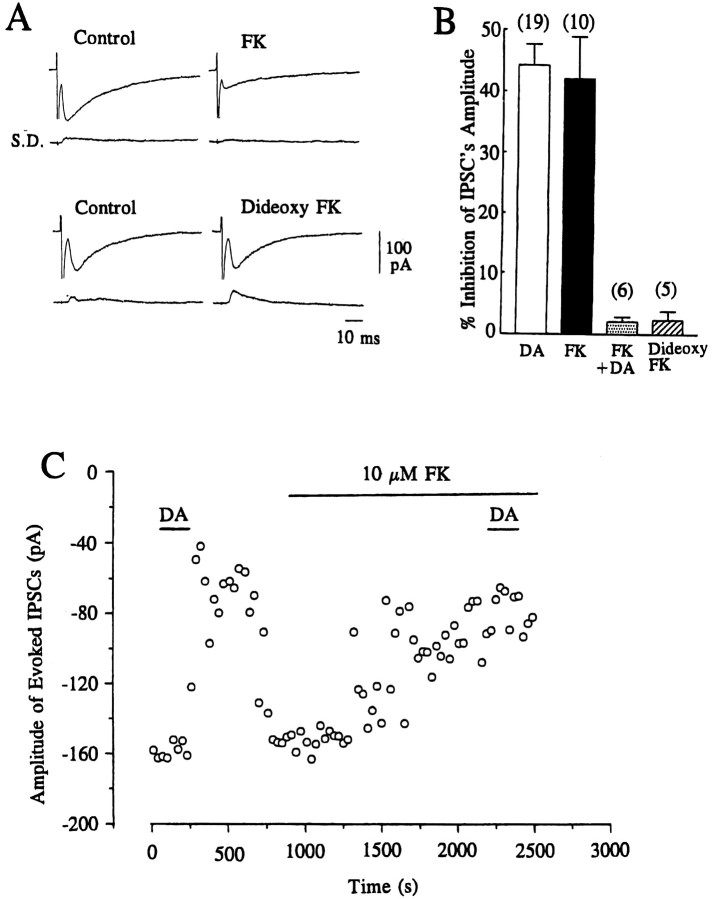
Fig. 4.
Effects of forskolin and 1,9-dideoxyforskolin on evoked IPSCs. A, Traces of evoked IPSCs showing the effect of forskolin (FK) and 1,9-dideoxyforskolin (Dideoxy FK). Each trace is the average of 10 consecutive responses evoked at 0.1 Hz with the corresponding SD. Current traces showing the effect of FK and dideoxy FK were derived from different cells. B, Summary histograms representing mean ± SEM of % inhibition of the amplitude of IPSCs by dopamine (DA, 10 μm), by FK (10 μm), by DA subsequent to 10–20 min perfusion of FK (FK+DA), and by Dideoxy FK. Values were 44.3 ± 3.4% (n = 19), 42.1 ± 6.8% (n = 10), 2.1 ± 0.76% (n= 6), and 2.4 ± 1.5% (n = 5), respectively. (The value for DA was derived from the concentration–response curve in Fig. 1.) There was no significant (p > 0.33) difference in the effect produced by DA compared with FK. The dideoxy FK-induced effect was significantly (p < 0.002) smaller than that of DA or FK. Application of 10 μm DA after the effect of FK had reached a steady level (after 15–20 min) produced virtually no further effect on the inhibitory action on the amplitude of IPSCs, and the effect of DA in the presence of FK was significantly (p < 0.001) smaller than that of DA or FK applied alone. C, Time course of the inhibitory effect of FK (10 μm) on the amplitude of evoked IPSCs and occlusion of the effect of DA (10 μm) in the continuing presence of FK. IPSCs were evoked at 0.1 Hz, and each point represents the mean amplitude of three consecutive responses. The holding potential was −70 mV.