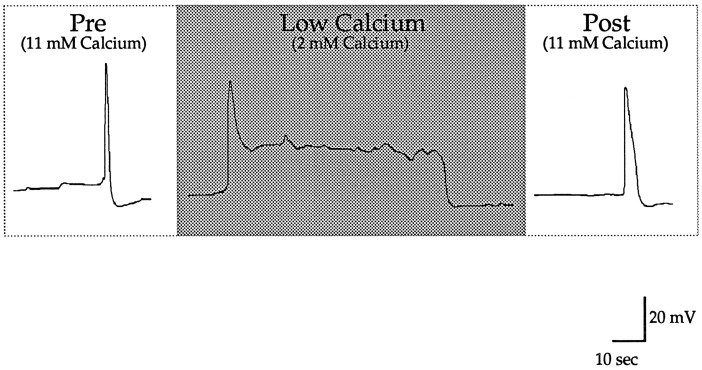
Fig. 4.
Extracellular calcium modulates the initial spike amplitude and the duration of TEA-induced prolonged depolarization. Artificial seawater normally contains 11 mm calcium. When the calcium concentration is lowered to 2 mm, the prolonged depolarizations induced by 75 mm TEA exhibit two changes: (1) decreased amplitude of the initial spike, and (2) increased duration of depolarization. Addition of barium to preserve the concentration of divalent cations does not affect the duration of depolarization. For quantitative group results, see text.