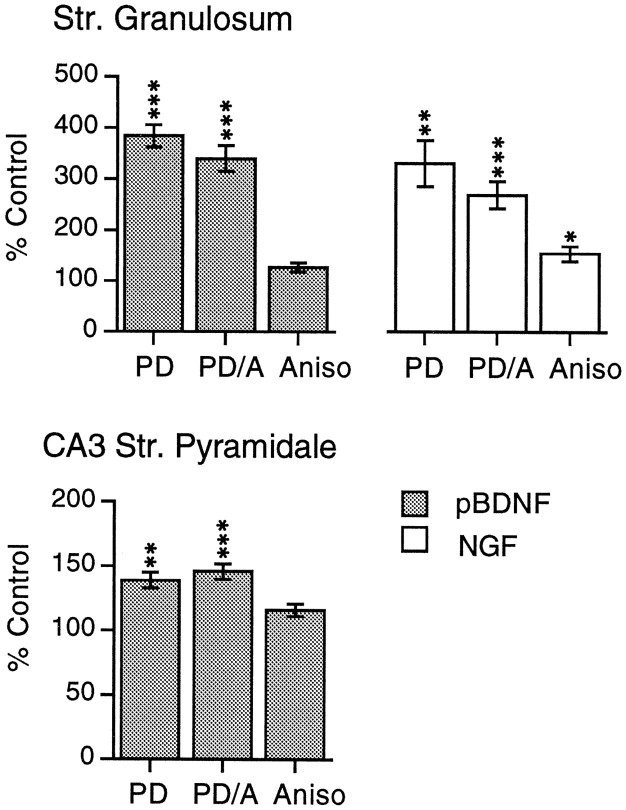
Fig. 2.
Quantification of PD-induced increases in BDNF and NGF mRNAs with and without protein synthesis inhibition. Bar graphs showing the densities of pan-BDNF cRNA (pBDNF) and NGF cRNA (NGF) labeling of stratum granulosum (top graphs) and CA3 stratum pyramidale (bottom graph) in rats receiving a PD alone (PD), a PD in the presence of anisomycin (PD/A), or anisomycin alone (Aniso). Density measures represent group means (± SE; n ≥ 5 per group) and are expressed as a percent of labeling density measures from paired control rats. For stratum granulosum, BDNF cRNA hybridization was increased to comparable levels in the PD and PD/A groups. For NGF cRNA, anisomycin increased hybridization when applied alone and slightly attenuated but did not prevent the increase in labeling elicited by a single PD. Significance levels calculated from raw data by ANOVA followed by Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test for BDNF and by Welch’s t test for NGF; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for comparison with control group.