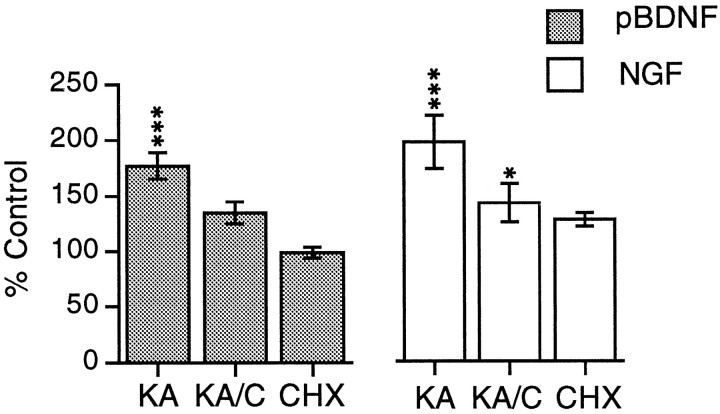
Fig. 4.
Quantification of kainic acid-induced increases in BDNF and NGF mRNA in hippocampal explants. Bar graphs showing measures of pan-BDNF cRNA (pBDNF) and NGF cRNA (NGF) labeling in the stratum granulosum in sections through cultured hippocampus treated with kainic acid alone (KA), kainic acid in the presence of CHX (KA/C), or CHX alone (CHX). Measures from drug-treated tissue are expressed as a percent of values from paired control explants. The values plotted represent group means ± SE for n = 7 per group for pan-BDNF and n = 4 per group for NGF. As determined from statistical analyses using raw measures, the effect of treatment was significant for both cRNAs (p < 0.001, ANOVA). In comparison with control (vehicle-treated) tissue, kainic acid increased mean hybridization densities when applied alone (***p < 0.001) or in the presence of CHX, although the latter was not statistically significant; labeling was significantly lower in the kainic acid/CHX group as compared with the kainic acid-alone group (p < 0.01). Similarly, for the NGF cRNA, kainic acid applied alone or in the presence of CHX increased granule cell labeling (***p < 0.001 and *p < 0.05, respectively, for comparison with control tissue), although with the combined treatment (KA/C), measures were lower than with kainic acid applied alone (KA; p < 0.01).