Fig. 1.
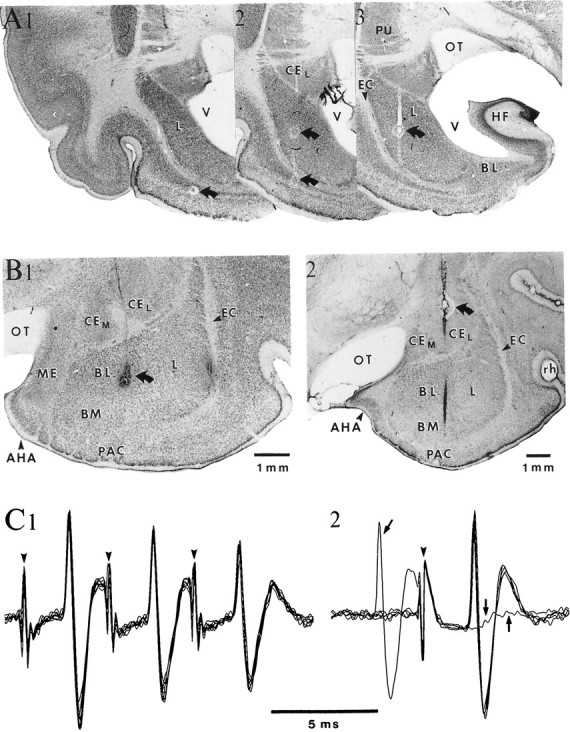
Histological localization and antidromic identification of neurons in the BL amygdaloid complex. A, Microelectrode track through the lateral nucleus on three consecutive frontal sections displayed from caudal (1) to rostral (3). B, Histological control of two microelectrode tracks (1–2) through the BL nucleus. InA and B, curved arrows point to electrolytic lesions performed to facilitate histological reconstruction of electrode tracks. C, ENT stimulation (arrowheads) elicits antidromic spikes in a neuron located in the caudal part of the BM nucleus. Note constant latency of antidromic responses, ability to follow high-frequency stimulation (C1), and collision with a spontaneous action potential (arrows in C2). AHA, Amygdalohippocampal area; HF, hippocampal formation;ME, medial amygdaloid nucleus; OT, optic tract;PAC, periamygdaloid cortex; PU, putamen;V, ventricle.
