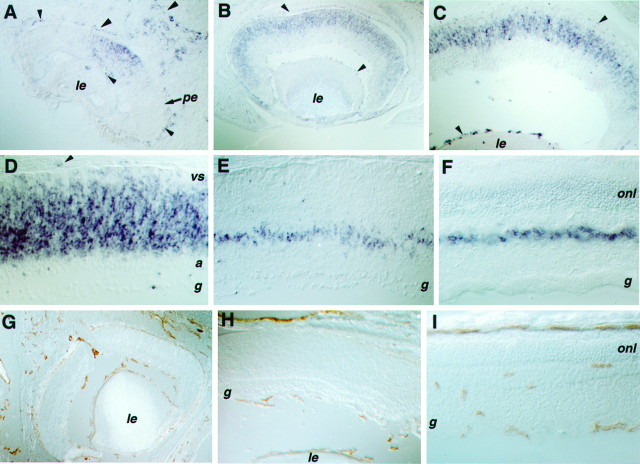
Fig. 2.
Expression of Flk-1 and CD31 in the developing eye. A–F, Tissue sections processed for in situ hybridizations using probes of Flk-1. G–I, Immunohistochemical staining of the endothelial cell-surface antigen CD31. A cross section of an E11.5 eye (A) displays the Flk-1 signal in the center of the neural retina, as well as in blood vessel networks of the eye (choroid and hyaloid). A cross section of an E15 eye (B) shows the spread of Flk-1 expression into the periphery of the retina. Cross sections of E17 eye (C) and P0 retina (D) display Flk-1 signal in the VZ of the retina. A cross section of a P7 retina (E) reveals more restricted expression of Flk-1 in the future inner nuclear layer. A cross section of an adult retina (F) shows limited Flk-1 expression in cells of the inner nuclear layer. Cross sections of E18 (G), P2 (H), and adult eye (I) stained with an anti-CD31 antibody reveal blood vessel formation in the mouse eye. Note that, at E18 and P2, blood vessels were seen in the choroid and hyaloid networks, but no endothelial cells were detected in the neural retina proper. Arrowheads indicate in situ hybridization signals in endothelial cells.le, Lens; vs, ventricular surface;a, differentiating amacrine cell layer;g, retinal ganglion cell layer; onl, outer nuclear layer; pe, pigmented epithelium.