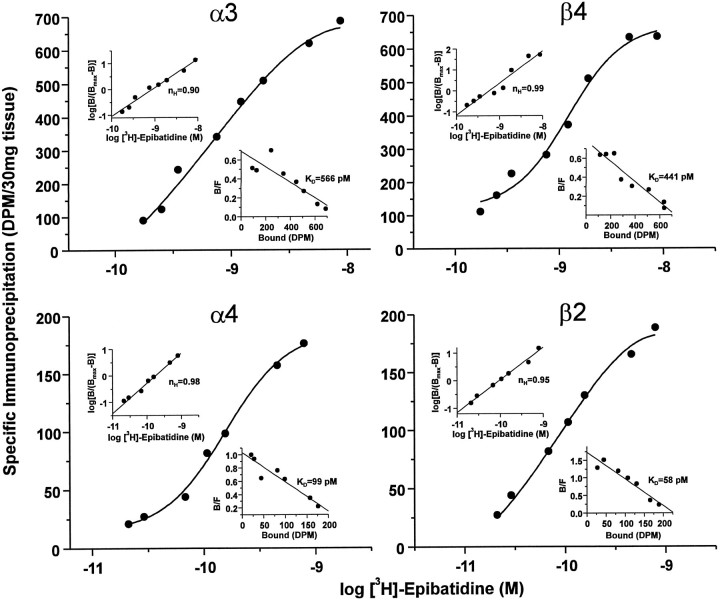
Fig. 4.
Binding parameters of neuronal nicotinic receptor subtypes in the rat trigeminal ganglion. Saturation binding analysis of neuronal nicotinic receptors labeled with [3H]-epibatidine and immunoprecipitated with subunit-specific rabbit antisera. Aliquots of Triton X-100-solubilized rat trigeminal ganglion membranes equivalent to 30 mg of original tissue weight were labeled with [3H]-epibatidine at the indicated concentrations (0.175–8.7 nm forα3 and β4; 29–792 pm forα4 and β2), incubated with rabbit antisera specific for each of the neuronal nicotinic receptor subunits indicated or normal rabbit serum (NRS), and then precipitated with Pansorbin cells by centrifugation. Specific immunoprecipitation was calculated to be the difference between that obtained with each subunit-specific serum and that obtained with NRS at each concentration of [3H]-epibatidine. Each quadrant depicts a semilog plot of the data for each of the four antisera tested, expressed as specific immunoprecipitation in dpm/30 mg of tissue. Top left insets, Hill plot, including the calculated Hill coefficient (nH), of the transformed data. Bottom right insets, Rosenthal plots, including calculated equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) values, of the transformed data. Data were analyzed by nonlinear regression with LIGAND (Munson and Rodbard, 1980) and, for each subunit, were best fit to a one-site model as indicated by the single solid lines (circles). Because of the tremendous amounts of tissue, radioactivity, and antibody required, this experiment was performed only once.