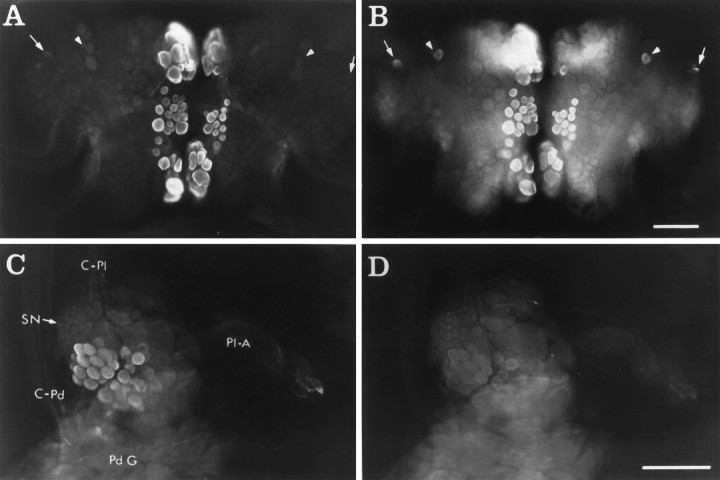
Fig. 4.
CP1-lir and CP2-lir in whole mounts.A, Ventral surface of the cerebral ganglia showing CP2-lir using GAR(IgG)-AMCA as the secondary antiserum.B, Same view as in A showing CP1-lir using GAR(Fab)-FITC as the secondary antiserum. In A andB, arrowheads indicate bilaterally symmetrical neurons in the M clusters, and arrowsindicate bilaterally symmetrical neurons in rostral E clusters that contain CP1-lir but no detectable CP2-lir. C, Medial surface of right pleural ganglion showing CP2-lir using GAR(Fab)-LR as the secondary antiserum. D, Same view as inC, showing CP1-lir using GAR(IgG)-FITC as the secondary antiserum. Medial pleural neurons contain CP2-lir but no detectable CP1-lir. Other immunoreactive neurons in the anterior region of the ganglion are out of the plane of focus (see Fig. 5).C-Pd, Cerebral–pedal connective; C-Pl, cerebral–pleural connective; Pd G, pedal ganglion;Pl-A, pleural–abdominal connective; SN, sensory neuron cluster. Scale bar, 200 μm.