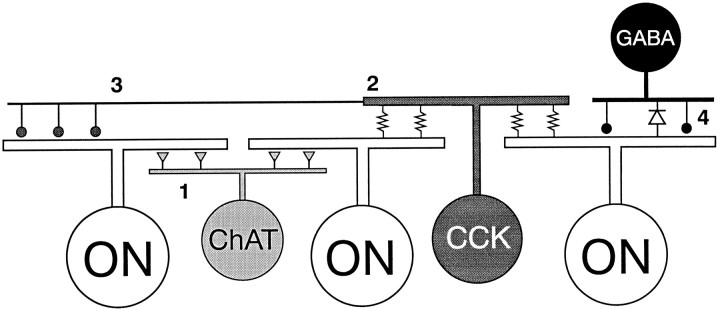
Fig. 18.
Summary diagram of the proposed synapses from amacrine cells to ON-parasol ganglion cells. The synapses of bipolar cells and the synapses between amacrine cells have been omitted. The displaced amacrine cell labeled ChAT (light gray) probably contains both acetylcholine and GABA (Rodieck and Marshak, 1992). Based on the actions of acetylcholine in cat retina, it is expected to make excitatory synapses (filled triangles) onto the ganglion cells (1). The larger displaced amacrine cell labeledCCK (dark gray) is G6-gly-positive and makes gap junctions (resistors) with the proximal dendrites of the ON-parasol cell at (2). It contains cholecystokinin and, possibly, GABA. Its axons make inhibitory synapses (filled circles) onto parasol ganglion cell dendrites, mainly those outside of its dendritic field (3). The amacrine cell labeled GABA in the inner nuclear layer (black) represents the smaller tracer-coupled amacrine cell. It might make both inhibitory synapses and rectified gap junctions (diodes) with the parasol ganglion cell dendrites (4). Dacey and Brace (1992) suggested that it might make gap junctions with the CCK amacrine cells rather than the parasol ganglion cells.