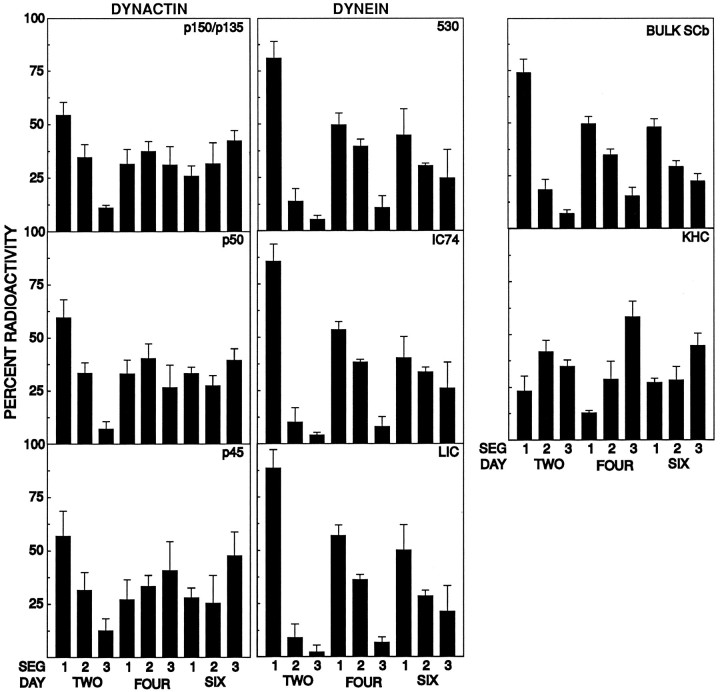
Fig. 3.
Quantitative comparison of the SCb transport segmental analysis of dynactin, cytoplasmic dynein, kinesin, and bulk protein. Dynactin, cytoplasmic dynein, and kinesin were immunoprecipitated sequentially from homogenates of individual segments of optic nerves removed at 2, 4, and 6 d after injection, as described above. Bulk SCb protein was determined from TCA-precipitable counts of radiolabeled tissue homogenates from the segments. Quantitation of the indicated polypeptides from the storage phosphor autoradiographs was performed with ImageQuant analysis software, as described in Materials and Methods. The average of three trials (n = 3) is shown. Left(DYNACTIN), Quantitation of the major radiolabeled dynactin subunit polypeptides: p150Glued and p135Gluedisoforms (p150/p135), p50, and Arp1 (p45). Center(DYNEIN), Quantitation of the cytoplasmic dynein subunit polypeptides: dynein heavy chain (530), the 74 kDa intermediate chain (IC74), and the 53–59 kDa set of light intermediate chains (LIC).Right, Top, Quantitation of bulk radioactive TCA-precipitable protein present in the rat optic nerve and tract (BULK SCb) at the indicated times after injection.Right, Center, Quantitation of the kinesin heavy chain (KHC). Dynactin and cytoplasmic dynein have transport kinetics consistent with SCb transport, as opposed to kinesin, representative of the transport kinetics of proteins transported with fast component.