Fig. 5.
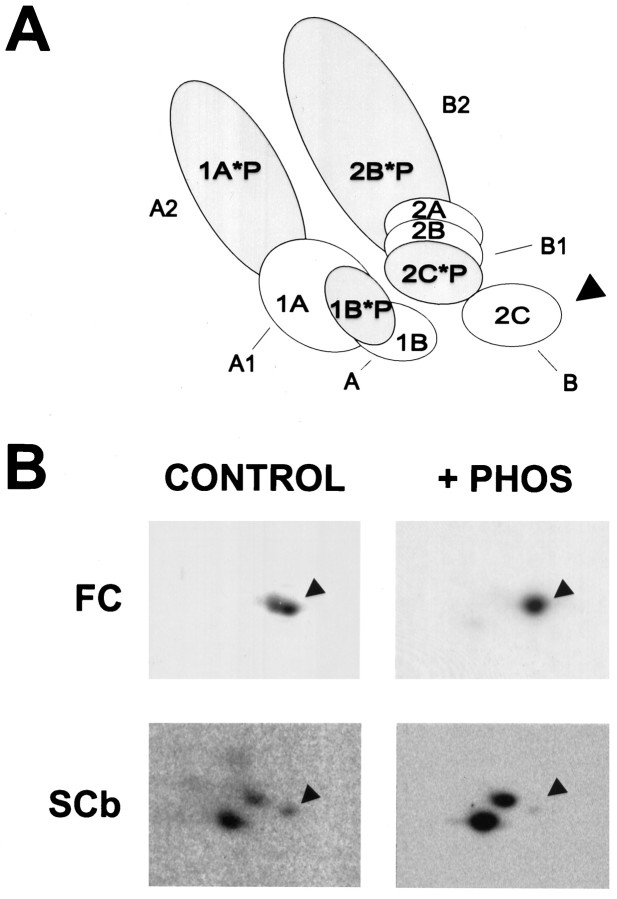
Identification of IC74 gene products associated with fast component and SCb by two-dimensional gel analysis and phosphatase treatment. A, Diagram showing IC74 isoforms from whole rat brain (Pfister et al., 1996a,b). The different gene products (IC74-1A, IC74-1B, IC74-2A, IC74-2B, IC74-2C) are indicatedinside the spots. The *Pdesignation inside the spots indicates phosphoisoforms. The protein spot designations of the A arc (A, A1, A2) and B arc (B, B1, B2) are indicatedoutside the spots. For orientation purposes, the arrowhead points to the B spot (IC74-2C gene product). B, Radiolabeled cytoplasmic dynein immunoprecipitated from fast component (FC; top 2 panels) and slow component b (SCb; bottom 2 panels). Equivalent samples of the immunoprecipitated dynein were treated with buffer alone (CONTROL) or with phosphatase (+ PHOS) and then analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and fluorography or storage phosphor autoradiography. For orientation purposes, the arrowhead points to the B spot (IC74-2C gene product). In the control dynein from fast component (top left), both IC74-2C and phospho-IC74-2C are seen, and phospho-IC74-2C is removed by phosphatase treatment, leaving IC74-2C (top right). Although barely detectable in these reproductions, there are faint spots in the A arc that did not reproduce well. In the dynein from SCb (bottom panels), all of the gene products and phosphoisoforms are present, although there is less IC74-2C (B spot, indicated by thearrow) than in whole brain (Pfister et al., 1996a,b), and the phosphoisoforms are removed by treatment with phosphatase.