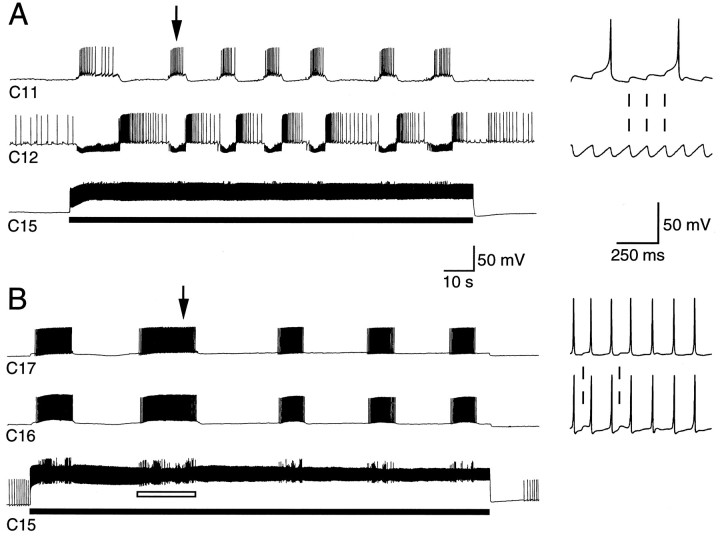
Fig. 3.
Input to cerebral lip motoneurons during the CMP in isolated cerebral ganglia. The CMP was driven by injecting constant depolarizing current into C15 (solid bars). A, M-cluster lip motoneurons C11 andC12 were active in alternation. C11 received EPSPs and C12 IPSPs. B, E-cluster lip motoneuronsC16 and C17 both received EPSPs during the CMP and fired at high frequency. C16 and C17 were electrically coupled to C15 (and each other; see Fig.2A) and so were also tonically depolarized throughout the current pulse. Arrows indicate points on the slow record from which the faster time-base records to the right were taken. These show that the PSPs in all neurons were one-for-one with PSPs in the others (examples joined by dashed lines), suggesting a common source. C15 also received phasic excitatory input during the CMP (e.g., open bar inB) that was largely masked by the current-induced spiking but was represented by a rise in the firing frequency and uneven spike amplitudes.