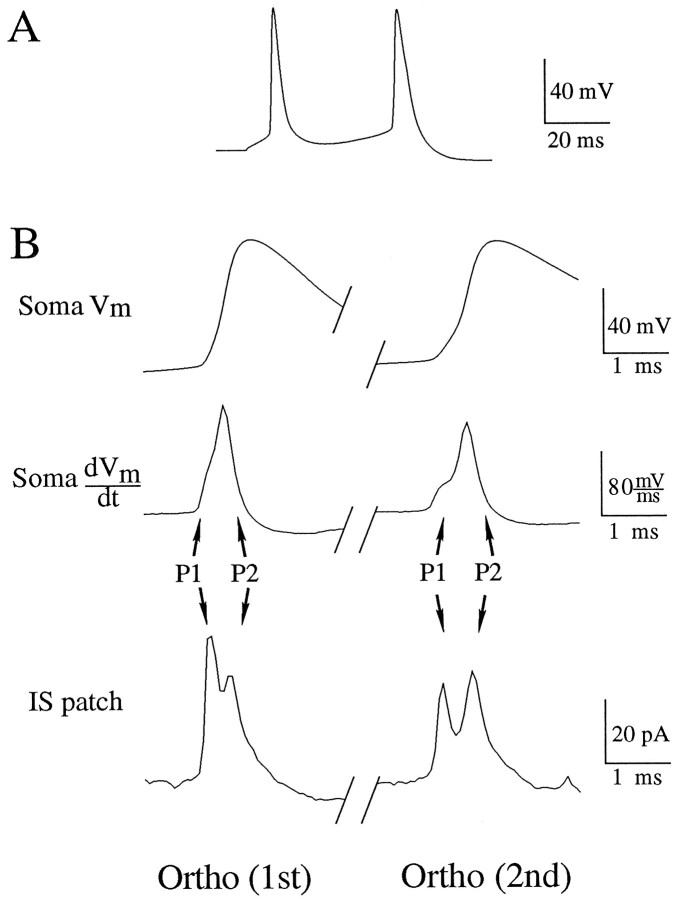
Fig. 4.
Sequence of orthodromic action-potential (AP) invasion of initial segment (IS) and soma. Dual-recording electrode positions are as in Figure 1. Waveforms are single sweeps.A, Somatic membrane potential recorded through the whole-cell electrode. Orthodromic action potentials were evoked by a 50 msec duration, 200 pA current injection through the recording electrode. B, Ortho (1st), Left column corresponds to the first action potential evoked by the orthodromic stimulus. Ortho (2nd), Right column corresponds to the second action potential initiated by the stimulus. Soma Vm, Membrane potential recorded through the somatic whole-cell electrode. Soma dVm/dt, Time derivative of the somatic membrane potential. IS patch, Cell-attached patch recording in the IS. The current recorded is primarily capacitive and, thus, is proportional to the time derivative of the transmembrane potential of the patch. P1 and P2 correspond to charging of the patch by channels in the initial segment and soma, respectively, as in Figure 3. Note that, although the peaks occur with shorter latency, the sequence of invasion of orthodromic APs is the same as that for antidromic APs. Cell c95066a.