Fig. 9.
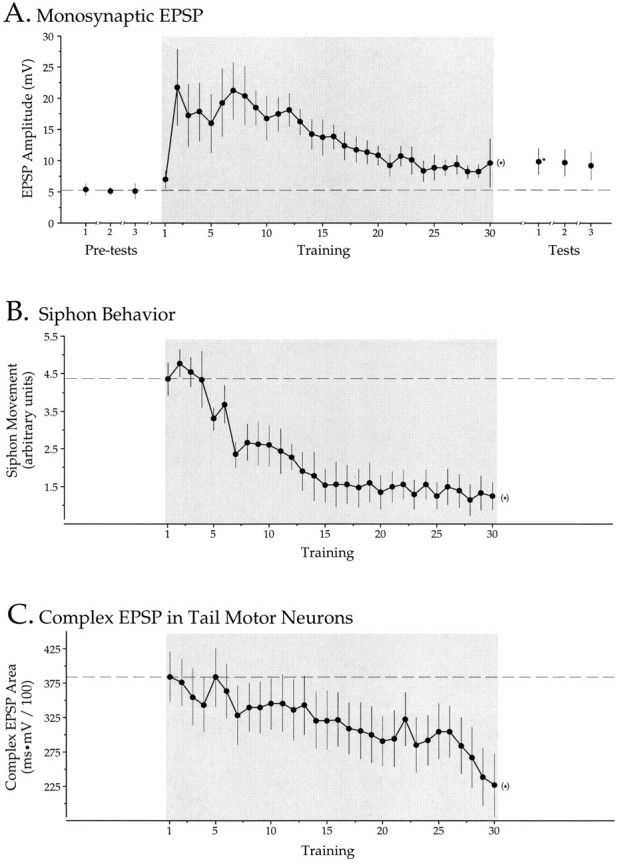
Habituation training facilitates sensory neuron synaptic transmission while simultaneously producing behavioral and motor neuronal decrement. A, Monosynaptic EPSPs from tail sensory neurons onto tail motor neurons were facilitated significantly over baseline response levels during training (shaded area). Pretests were conducted 15, 10, and 5 min before training. Intracellularly stimulated post-tests were conducted 1, 5, and 10 min after training. B, Replotted from Figure 4A. During training (shaded areas), the simultaneously monitored siphon withdrawal reflex habituated significantly, and (C) the complex EPSP recorded in the tail motor neurons also decremented significantly. (Dashed lines = initial response levels.) Tail stimulus pre- and post-tests were not delivered because they would have confounded the intracellular tests (see A) by facilitating the synapse. See legend to Figure 2 for statistical significance indicated by asterisks.
